Page 68 - IJB-7-3
P. 68
Heart-on-a-chip
A
B C
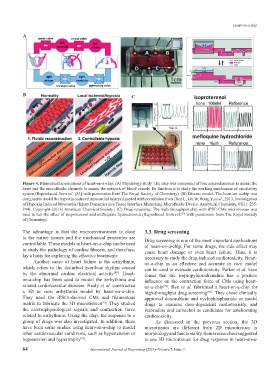
Figure 4. Biomedical applications of heart-on-a-chip. (A) Physiology study. The chip was composed of four microchambers to mimic the
heart and the microfluidic channels to mimic the network of blood vessels. Its function is to study the working mechanism of circulatory
system (Reproduced from ref. [83] with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry). (B) Disease model. The heart-on-a-chip was
designed to model the hypoxia-induced myocardial injury(Adapted with permission from (Ren L, Liu W, Wang Y, et al., 2013, Investigation
of Hypoxia-Induced Myocardial Injury Dynamics in a Tissue Interface Mimicking Microfluidic Device. Analytical Chemistry, 85(1): 235-
244). Copyright (2013) American Chemical Society.) (C) Drug screening. The high-throughput chip with iPSC-CMs microtissues was
used to test the effect of isoproterenol and mefloquine hydrochloride (Reproduced from ref. with permission from The Royal Society
[72]
of Chemistry).
The advantage is that the microenvironment is close 3.3. Drug screening
to the native tissues and the mechanical properties are Drug screening is one of the most important applications
controllable. These models in heart-on-a-chip can be used of heart-on-a-chip. For some drugs, the side effect may
to study the pathology of cardiac fibrosis, and therefore, cause heart damage or even heart failure. Thus, it is
lay a basis for exploring the effective treatments. necessary to study the drug-induced cardiotoxicity. Heart-
Another cause of heart failure is the arrhythmia, on-a-chip as an effective and accurate in vitro model
which refers to the disturbed heartbeat rhythm caused can be used to evaluate cardiotoxicity. Parker et al. have
by the abnormal cardiac electrical activity . Heart- found that the isopropylnoradrenaline has a positive
[89]
on-a-chip has been used to model the arrhythmia and influence on the contraction force of CMs using heart-
related cardiovascular diseases. Healy et al. constructed on-a-chip . Ren et al. fabricated a heart-on-a-chip for
[59]
a 3D in vitro arrhythmia model by heart-on-a-chip. high-throughput drug screening . They chose clinically
[92]
They used the iPSCs-derived CMs and filamentous approved doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide as model
matrix to fabricate the 3D microtissues . They studied drugs to examine dose-dependent cardiotoxicity, and
[90]
the electrophysiological signals and contraction force ivabradine and carbachol as candidates for ameliorating
related to arrhythmia. Using the chip, the response to a cardiotoxicity.
group of drugs was also investigated. In addition, there As discussed in the previous section, the 3D
have been some studies using heart-on-a-chip to model microtissues are different from 2D microtissues in
other cardiovascular conditions, such as hypertension or morphology and functionality. Some researchers suggested
hypotension and hypertrophy . to use 3D microtissues for drug response in heart-on-a-
[91]
64 International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 3