Page 82 - IJB-7-3
P. 82
Fabrication of Layered Gradient Brain-like Tissue by 3D Bioprinting
A B
C D
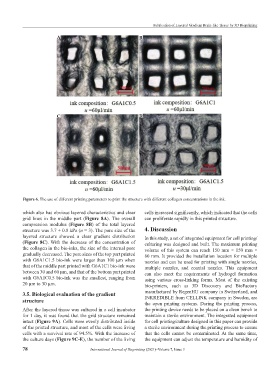
Figure 6. The use of different printing parameters to print the structure with different collagen concentrations in the ink.
which also has obvious layered characteristics and clear cells increased significantly, which indicated that the cells
grid lines in the middle part (Figure 8A). The overall can proliferate rapidly in this printed structure.
compression modulus (Figure 8B) of the total layered
structure was 3.7 ± 0.8 kPa (n = 3). The pore size of the 4. Discussion
layered structure showed a clear gradient distribution In this study, a set of integrated equipment for cell printing/
(Figure 8C). With the decrease of the concentration of culturing was designed and built. The maximum printing
the collagen in the bio-inks, the size of the internal pore volume of this system can reach 150 mm × 150 mm ×
gradually decreased. The pore sizes of the top part printed 80 mm. It provided the installation location for multiple
with G6A1C1.5 bio-ink were larger than 100 μm when nozzles and can be used for printing with single nozzles,
that of the middle part printed with G6A1C1 bio-ink were multiple nozzles, and coaxial nozzles. This equipment
between 30 and 60 μm, and that of the bottom part printed can also meet the requirements of hydrogel formation
with G6A1C0.5 bio-ink was the smallest, ranging from using various cross-linking forms. Most of the existing
20 μm to 30 μm. bio-printers, such as 3D Discovery and BioFactory
3.5. Biological evaluation of the gradient manufactured by RegenHU company in Switzerland, and
structure INKREDIBLE from CELLINK company in Sweden, are
the open printing systems. During the printing process,
After the layered tissue was cultured in a cell incubator the printing device needs to be placed on a clean bench to
for 1 day, it was found that the grid structure remained maintain a sterile environment. The integrated equipment
intact (Figure 9A). Cells were evenly distributed inside for cell printing/culture designed in this paper can provide
of the printed structure, and most of the cells were living a sterile environment during the printing process to ensure
cells with a survival rate of 94.5%. With the increase of that the cells cannot be contaminated. At the same time,
the culture days (Figure 9C-E), the number of the living the equipment can adjust the temperature and humidity of
78 International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 3