Page 116 - IJB-8-1
P. 116
Antibacterial Performance of Graphene Oxide-loaded Nickel
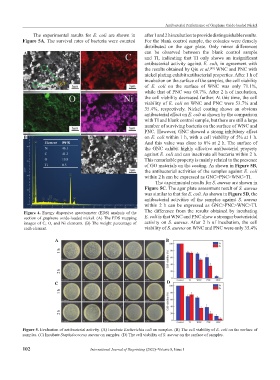
The experimental results for E. coli are shown in after 1 and 2 h incubation to provide distinguishable results.
Figure 5A. The survival rates of bacteria were counted For the blank control sample, the colonies were densely
distributed on the agar plate. Only minor differences
A can be observed between the blank control sample
and TI, indicating that TI only shows an insignificant
antibacterial activity against E. coli, in agreement with
the results obtained by Qiu et al. WNC and PNC with
[49]
nickel plating exhibit antibacterial properties. After 1 h of
incubation on the surface of the samples, the cell viability
of E. coli on the surface of WNC was only 71.1%,
while that of PNC was 60.7%. After 2 h of incubation,
the cell viability decreased further. At this time, the cell
viability of E. coli on WNC and PNC were 53.7% and
35.4%, respectively. Nickel coating shows an obvious
antibacterial effect on E. coli as shown by the comparison
with TI and blank control sample, but there are still a large
number of surviving bacteria on the surface of WNC and
PNC. However, GNC showed a strong inhibitory effect
B on E. coli within 1 h, with a cell viability of 5% at 1 h.
And this value was close to 0% at 2 h. The surface of
the GNC exhibit highly effective antibacterial property
against E. coli and can inactivate all bacteria within 2 h.
This remarkable property is mainly related to the presence
of GO materials on the coating. As shown in Figure 5B,
the antibacterial activities of the samples against E. coli
within 2 h can be expressed as GNC>PNC>WNC>TI.
The experimental results for S. aureus are shown in
Figure 5C. The agar plate assessment result of S. aureus
was similar to that for E. coli. As shown in Figure 5D, the
antibacterial activities of the samples against S. aureus
within 2 h can be expressed as GNC>PNC>WNC>TI.
Figure 4. Energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) analysis of the The difference from the results obtained by incubating
section of graphene oxide-loaded nickel. (A) The EDS mapping E. coli is that WNC and PNC show a stronger bactericidal
images of C, O, and Ni elements. (B) The weight percentage of activity on S. aureus. After 2 h of incubation, the cell
each element. viability of S. aureus on WNC and PNC were only 35.4%
A B
C D
Figure 5. Evaluation of antibacterial activity. (A) Incubate Escherichia coli on samples. (B) The cell viability of E. coli on the surface of
samples. (C) Incubate Staphylococcus aureus on samples. (D) The cell viability of S. aureus on the surface of samples.
102 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 1