Page 120 - IJB-8-1
P. 120
Antibacterial Performance of Graphene Oxide-loaded Nickel
A B
C D
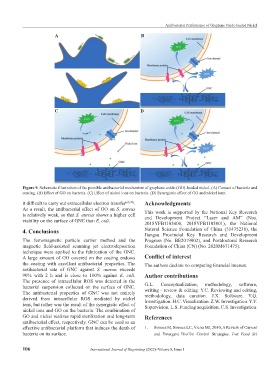
Figure 9. Schematic illustration of the possible antibacterial mechanism of graphene oxide (GO)-loaded nickel. (A) Contact of bacteria and
coating. (B) Effect of GO on bacteria. (C) Effect of nickel ions on bacteria. (D) Synergistic effect of GO and nickel ions.
it difficult to carry out extracellular electron transfer [69,70] . Acknowledgments
As a result, the antibacterial effect of GO on S. aureus This work is supported by the National Key Research
is relatively weak, so that S. aureus shows a higher cell and Development Project “Laser and AM” (Nos.
viability on the surface of GNC than E. coli. 2018YFB1105400, 2018YFB1105801), the National
4. Conclusions Natural Science Foundation of China (51475238), the
Jiangsu Provincial Key Research and Development
The ferromagnetic particle carrier method and the Program (No. BE2019002), and Postdoctoral Research
magnetic field-assisted scanning jet electrodeposition Foundation of China (CN) (No. 2020M671475).
technique were applied to the fabrication of the GNC.
A large amount of GO covered on the coating endows Conflict of interest
the coating with excellent antibacterial properties. The The authors declare no competing financial interest.
antibacterial rate of GNC against S. aureus exceeds
90% with 2 h and is close to 100% against E. coli. Author contributions
The presence of intracellular ROS was detected in the
bacterial suspension collected on the surface of GNC. G.L. Conceptualization, methodology, software,
The antibacterial properties of GNC was not entirely writing - review & editing. Y.C. Reviewing and editing,
methodology, data curation. J.X. Software. Y.Q.
derived from intracellular ROS mediated by nickel Investigation. H.C. Visualization. Z.W. Investigation. Y.Y.
ions, but rather was the result of the synergistic effect of Supervision. L.S. Funding acquisition. C.S. Investigation.
nickel ions and GO on the bacteria. The combination of
GO and nickel realizes rapid sterilization and long-term References
antibacterial effect, respectively. GNC can be used as an
effective antibacterial platform that induces the death of 1. Simoes M, Simoes LC, Vieira MJ, 2010, A Review of Current
bacteria on its surface. and Emergent Biofilm Control Strategies. Lwt Food Sci
106 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 1