Page 117 - IJB-8-1
P. 117
Lou, et al.
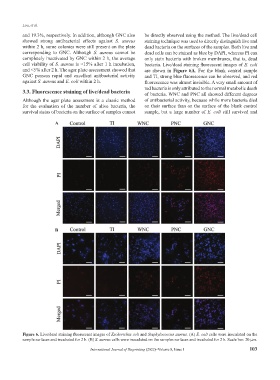
and 19.3%, respectively. In addition, although GNC also be directly observed using the method. The live/dead cell
showed strong antibacterial effects against S. aureus staining technique was used to directly distinguish live and
within 2 h, some colonies were still present on the plate dead bacteria on the surfaces of the samples. Both live and
corresponding to GNC. Although S. aureus cannot be dead cells can be stained as blue by DAPI, whereas PI can
completely inactivated by GNC within 2 h, the average only stain bacteria with broken membranes, that is, dead
cell viability of S. aureus is <15% after 1 h incubation, bacteria. Live/dead staining fluorescent images of E. coli
and <5% after 2 h. The agar plate assessment showed that are shown in Figure 6A. For the blank control sample
GNC possess rapid and excellent antibacterial activity and TI, strong blue fluorescence can be observed, and red
against S. aureus and E. coli within 2 h. fluorescence was almost invisible. A very small amount of
red bacteria is only attributed to the normal metabolic death
3.3. Fluorescence staining of live/dead bacteria of bacteria. WNC and PNC all showed different degrees
Although the agar plate assessment is a classic method of antibacterial activity, because while more bacteria died
for the evaluation of the number of alive bacteria, the on their surface than on the surface of the blank control
survival status of bacteria on the surface of samples cannot sample, but a large number of E. coli still survived and
A
B
Figure 6. Live/dead staining fluorescent images of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. (A) E. coli cells were inoculated on the
sample surfaces and incubated for 2 h. (B) S. aureus cells were inoculated on the samples surfaces and incubated for 2 h. Scale bar: 20 μm.
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 1 103