Page 59 - IJB-8-2
P. 59
Chand, et al.
A B
C
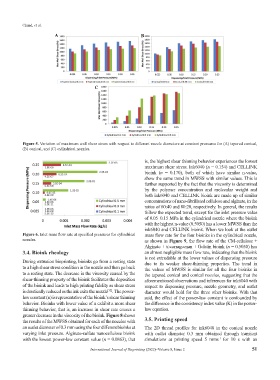
Figure 5. Variation of maximum wall shear stress with respect to different nozzle diameters at constant pressures for (A) tapered conical,
(B) conical, and (C) cylindrical nozzles.
is, the highest shear thinning behavior experiences the lowest
maximum shear stress. Ink6040 (n = 0.154) and CELLINK
bioink (n = 0.170), both of which have similar n-value,
show the same trend in MWSS with similar values. This is
further supported by the fact that the viscosity is determined
by the polymer concentration and molecular weight and
both ink6040 and CELLINK bioink are made up of similar
concentrations of nano-fibrillated cellulose and alginate, in the
ratios of 60:40 and 80:20, respectively. In general, the results
follow the expected trend, except for the inlet pressure value
of 0.05–0.15 MPa in the cylindrical nozzle where the bioink
with the highest n-value (0.5050) has a lower MWSS than the
ink6040 and CELLINK bioink. When we look at the outlet
Figure 6. Inlet mass flow rate at specified pressures for cylindrical mass flow rate for the four bioinks in the cylindrical nozzle,
nozzles. as shown in Figure 9, the flow rate of the CM-cellulose +
Alginate + κ-carrageenan + Gelatin bioink (n = 0.5050) has
3.4. Bioink rheology an almost negligible mass flow rate, indicating that the bioink
is not extrudable at the lower values of dispensing pressure
During extrusion bioprinting, bioinks go from a resting state due to its weaker shear-thinning properties. The trend in
to a high shear stress condition in the nozzle and then go back the values of MWSS is similar for all the four bioinks in
to a resting state. The decrease in the viscosity caused by the the tapered conical and conical nozzles, suggesting that the
shear-thinning property of the bioink facilitates the deposition aforementioned observations and inferences for ink6040 with
of the bioink and leads to high printing fidelity as shear stress respect to dispensing pressure, nozzle geometry, and outlet
is drastically reduced as the ink exits the nozzle . The power- diameter would hold for the three other bioinks. With that
[32]
law constant (n) is representative of the bioink’s shear thinning said, the effect of the power-law constant is confounded by
behavior. Bioinks with lower value of n exhibit a more shear the difference in the consistency index value (K) in the power-
thinning behavior, that is, an increase in shear rate causes a law equation.
greater decrease in the viscosity of the bioink. Figure 8 shows
the results of the MWSS obtained for each of the nozzles with 3.5. Printing speed
an outlet diameter of 0.3 mm using the four different bioinks at The 2D thread profiles for ink6040 in the conical nozzle
varying inlet pressure. Alginate-sulfate nanocellulose bioink with outlet diameter 0.3 mm obtained through transient
with the lowest power-law constant value (n = 0.0863), that simulations at printing speed 5 mms for 10 s with an
−1
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 2 51