Page 93 - IJB-8-2
P. 93
Wang, et al.
A B
C
D
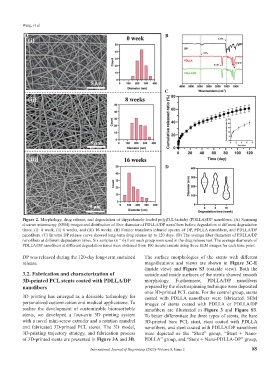
Figure 2. Morphology, drug release, and degradation of dipyridamole-loaded poly(D,L-lactide) (PDLLA)/DP nanofibers. (A) Scanning
electron microscopy (SEM) images and distribution of fiber diameter of PDLLA/DP nanofibers before degradation at different degradation
times: (i): 0 week, (ii) 8 weeks, and (iii) 16 weeks. (B) Fourier transform infrared spectra of DP, PDLLA nanofibers, and PDLLA/DP
nanofibers. (C) In vitro DP release curve showed long-term drug release up to 120 days. (D) The average fiber diameters of PDLLA/DP
nanofibers at different degradation times. Six samples (n = 6) from each group were used in the drug release test. The average diameters of
PDLLA/DP nanofibers at different degradation times were obtained from 100 measurements using three SEM images for each time point.
DP was released during the 120-day long-term sustained The surface morphologies of the stents with different
release. magnifications and views are shown in Figure 3C-E
(inside view) and Figure S3 (outside view). Both the
3.2. Fabrication and characterization of outside and inside surfaces of the stents showed smooth
3D-printed PCL stents coated with PDLLA/DP morphology. Furthermore, PDLLA/DP nanofibers
nanofibers prepared by the electrospinning technique were deposited
onto 3D-printed PCL stents. For the control group, stents
3D printing has emerged as a desirable technology for coated with PDLLA nanofibers were fabricated. SEM
personalized customization and medical applications. To images of stents coated with PDLLA or PDLLA/DP
realize the development of customizable bioresorbable nanofibers are illustrated in Figure 3 and Figure S3.
stents, we developed a four-axis 3D printing system To better differentiate the three types of stents, the bare
with a novel mini-screw extruder and a rotation mandrel 3D-printed bare PCL stent, stent coated with PDLLA
and fabricated 3D-printed PCL stents. The 3D model, nanofibers, and stent coated with PDLLA/DP nanofibers
3D-printing trajectory strategy, and fabrication process were depicted as the “Stent” group, “Stent + Nano-
of 3D-printed stents are presented in Figure 3A and 3B. PDLLA” group, and “Stent + Nano-PDLLA-DP” group,
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 2 85