Page 175 - IJB-8-3
P. 175
Ma, et al.
A B C
D E
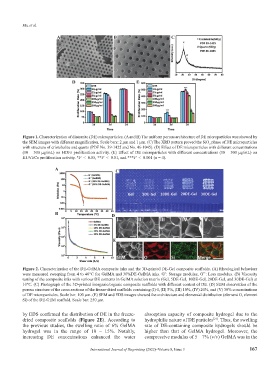
Figure 1. Characterization of diatomite (DE) microparticles. (A and B) The uniform porous architecture of DE microparticles was showed by
the SEM images with different magnification. Scale bars: 2 μm and 1 μm. (C) The XRD pattern proved the SiO phase of DE microparticles
2
with structure of cristobalite and quartz (PDF No. 39-1425 and No. 46-1045). (D) Effect of DE microparticles with different concentrations
(10 – 500 μg/mL) on HDFs proliferation activity. (E) Effect of DE microparticles with different concentrations (10 – 500 μg/mL) on
HUVECs proliferation activity. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 (n = 4).
A C
B D
E
Figure 2. Characterization of the DE-GelMA composite inks and the 3D-printed DE-Gel composite scaffolds. (A) Rheological behaviors
were measured sweeping from 4 to 40°C for GelMA and 30%DE-GelMA inks. G’: Storage modulus, G’’: Loss modulus. (B) Viscosity
testing of the composite inks with various DE contents in GelMA solution matrix (Gel, 5DE-Gel, 10DE-Gel, 20DE-Gel, and 30DE-Gel) at
10°C. (C) Photograph of the 3D-printed inorganic/organic composite scaffolds with different content of DE. (D) SEM observation of the
porous structure of the cross sections of the freeze-dried scaffolds containing (I) 0, (II) 5%, (III) 10%, (IV) 20%, and (V) 30% concentrations
of DE microparticles. Scale bar: 100 μm. (E) SEM and EDS images showed the architecture and elemental distribution (element O, element
Si) of the DE-GEM scaffold. Scale bar: 250 μm.
by EDS confirmed the distribution of DE in the freeze- absorption capacity of composite hydrogel due to the
dried composite scaffolds (Figure 2E). According to hydrophilic nature of DE particles [21] . Thus, the swelling
the previous studies, the swelling ratio of 6% GelMA rate of DE-containing composite hydrogels should be
hydrogel was in the range of 10 – 15%. Notably, higher than that of GelMA hydrogel. Moreover, the
increasing DE concentrations enhanced the water compressive modulus of 5 – 7% (v/v) GelMA was in the
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 3 167