Page 178 - IJB-8-3
P. 178
Composite Scaffolds for Skin Repair
A B
C
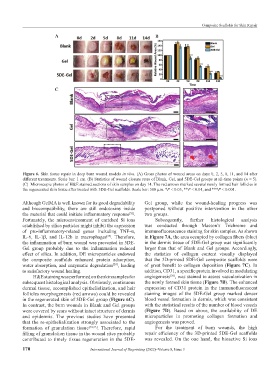
Figure 6. Skin tissue repair in deep burn wound models in vivo. (A) Gross photos of wound areas on days 0, 2, 5, 8, 11, and 14 after
different treatments. Scale bar: 1 cm. (B) Statistics of wound closure rates of Blank, Gel, and 5DE-Gel groups at all-time points (n = 5).
(C) Microscopic photos of H&E stained sections of skin samples on day 14. The red arrows marked several newly formed hair follicles in
the regenerated skin tissue after treated with 5DE-Gel scaffolds. Scale bar: 500 μm. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.
Although GelMA is well known for its good degradability Gel group, while the wound-healing progress was
and biocompatibility, there are still endotoxins inside postponed without positive intervention in the other
the material that could initiate inflammatory response . two groups.
[52]
Fortunately, the microenvironment of enriched Si ions Subsequently, further histological analysis
established by silica particles might inhibit the expression was conducted through Masson’s Trichrome and
of pro-inflammatory-related genes including TNF-α, immunofluorescence staining for skin samples. As shown
IL-6, IL-1β, and IL-12b in macrophages . Therefore, in Figure 7A, the area occupied by collagen fibers (blue)
[53]
the inflammation of burn wound was prevented in 5DE- in the dermis tissue of 5DE-Gel group was significantly
Gel group probably due to the inflammation reduced larger than that of Blank and Gel groups. Accordingly,
effect of silica. In addition, DE microparticles endowed the statistics of collagen content visually displayed
the composite scaffolds enhanced protein adsorption, that the 3D-printed 5DE-Gel composite scaffolds were
water absorption, and enzymatic degradation , leading of great benefit to collagen deposition (Figure 7C). In
[20]
to satisfactory wound healing. addition, CD31, a specific protein involved in modulating
H&E staining was performed on the skin samples for angiogenesis , was stained to assess vascularization in
[56]
subsequent histological analysis. Obviously, continuous the newly formed skin tissue (Figure 7B). The enhanced
dermal tissue, accomplished epithelialization, and hair expression of CD31 protein in the immunofluorescent
follicles morphogenesis (red arrows) could be revealed staining images of the 5DE-Gel group marked denser
in the regenerated skin of 5DE-Gel group (Figure 6C). blood vessel formation in dermis, which was consistent
In contrast, the burn wounds in Blank and Gel groups with the statistical results of the number of blood vessels
were covered by scars without intact structure of dermis (Figure 7D). Based on above, the availability of DE
and epidermis. The previous studies have presented microparticles in promoting collagen formation and
that the re-epithelialization strongly associated to the angiogenesis was proved.
formation of granulation tissue [54,55] . Therefore, rapid For the treatment of burn wounds, the high
filling of granulation tissue in the wound sites probably repair efficiency of the 3D-printed 5DE-Gel scaffolds
contributed to timely tissue regeneration in the 5DE- was revealed. On the one hand, the bioactive Si ions
170 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 3