Page 177 - IJB-8-3
P. 177
Ma, et al.
A B regulator of endothelial cell, was also stimulated because
its role in mediating diverse bioactivities of VEGF [47,48] .
The previous studies indicated that the increased pH
value contributed to the enhancement rate of natural silica
degradation . There is general agreement that dissolution
[49]
of silica at near-neutral pH is due to the breaking of Si-
O-Si siloxane bonds on the surface of particles that
attacked by water molecules . The increase of pH value
[50]
led to the deprotonation of surface silanol groups, which
further facilitated the breaking of the bridging Si-O-Si
bonds. Therefore, the degradation behavior of DE will
be obviously promoted under alkaline conditions, and the
concentration of Si ion released from the scaffolds will
increase probably.
Based on above, the incorporation of 5% DE
microparticles endowed 3D-printed composite scaffolds
with excellent abilities to promote proliferation and
C D vascularization of HUVECs significantly. Therefore, the
3D-printed 5DE-Gel scaffold was selected as an optimal
composite wound dressing with high bioactivity for
subsequent experiments.
3.4. Skin repair of deep burn wounds in vivo
Encouraged by the satisfactory bioactivities of the
3D-printed 5DE-Gel composite scaffolds, animal models
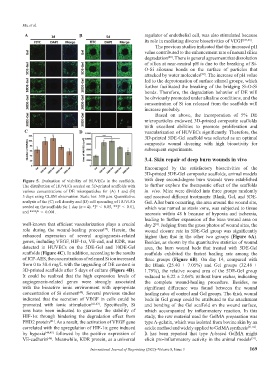
Figure 5. Evaluation of viability of HUVECs in the scaffolds. with deep second-degree burn wounds were established
The distribution of HUVECs seeded on 3D-printed scaffolds with to further explore the therapeutic effect of the scaffolds
various concentrations of DE microparticles for (A) 1 and (B) in vivo. Mice were divided into three groups randomly
5 days using CLSM observation. Scale bar: 500 μm. Quantitative and received different treatments: Blank, Gel, and 5DE-
analysis of the (C) cell density and (D) cell spreading of HUVECs Gel. After burn occurring, the area around the wound site,
seeded on the scaffolds for 1 day (n = 4). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, which was named as stasis zone, was subjected to tissue
and ***P < 0.001. necrosis within 48 h because of hypoxia and ischemia,
leading to further expansion of the burn wound area on
well-known that efficient vascularization plays a crucial day 2 . Judging from the gross photos of wound sites, the
[4]
role during the wound-healing process . Herein, the wound closure rate in 5DE-Gel group was significantly
[39]
enhanced expression of several angiogenesis-related higher than that in the other two groups (Figure 6A).
genes, including VEGF, HIF-1α, VE-cad, and KDR, was Besides, as shown by the quantitative statistics of wound
detected in HUVECs on the 5DE-Gel and 10DE-Gel area, the burn wound beds that treated with 5DE-Gel
scaffolds (Figure 4C). In addition, according to the results scaffolds exhibited the fastest healing rate among the
of ICP-AES, the concentrations of released Si ion increased three groups (Figure 6B). On day 14, compared with
from 0 to 38.4 mg/L with the upgrading of DE content in the Blank (25.40 ± 7.05%) and Gel groups (32.48 ±
3D-printed scaffolds after 5 days of culture (Figure 4D). 1.79%), the relative wound area of the 5DE-Gel group
It could be realized that the high expression levels of reduced to 6.22 ± 2.04% without burn eschar, indicating
angiogenesis-related genes were strongly associated the complete wound-healing procedure. Besides, no
with the bioactive ionic environment with appropriate significant difference was found between the wound
concentration of Si element . Several previous studies healing rates of control and Gel groups. The thick wound
[40]
indicated that the secretion of VEGF in cells could be beds in Gel group could be attributed to the attachment
promoted with ionic stimulation [41-43] . Specifically, Si and bonding of the Gel scaffold on the wound surface,
ions have been indicated to guarantee the stability of which accompanied by inflammatory reaction. In this
HIF-1α through hindering the degradation effect from study, the raw material used for GelMA preparation was
PHD2 protein . As a result, the activation of VEGF gene type A-gelatin, which was isolated from bovine skin by an
[41]
correlated with the upregulation of HIF-1α gene induced acidic method and widely applied to GelMA synthesis [51,52] .
by hypoxia [44,45] followed by the positive expression of It has been reported that type A-based GelMA might
VE-cadherin . Meanwhile, KDR protein, as a universal elicit pro-inflammatory activity in the animal models .
[51]
[46]
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 3 169