Page 234 - IJB-8-4
P. 234
3DP PEEK implants for chest wall reconstruction
A B C
D E F
G H I
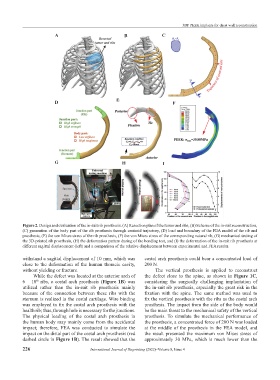
Figure 2. Design and evaluation of the in-suit rib prosthesis. (A) Resection plan of the tumor and ribs, (B) Scheme of the in-suit reconstruction,
(C) generation of the body part of the rib prosthesis through centroid trajectory, (D) load and boundary of the FEA model of the rib and
prosthesis, (E) the von Mises stress of the rib prosthesis, (F) the von Mises stress of the corresponding natural rib, (G) mechanical testing of
the 3D-printed rib prosthesis, (H) the deformation pattern during of the bending test, and (I) the deformation of the in-suit rib prosthesis at
different sagittal displacement (left) and a comparison of the relative displacement between experimental and FEA results.
withstand a sagittal displacement of 10 mm, which was costal arch prosthesis could bear a concentrated load of
close to the deformation of the human thoracic cavity, 200 N.
without yielding or fracture. The vertical prosthesis is applied to reconstruct
While the defect was located at the anterior arch of the defect close to the spine, as shown in Figure 1C,
6 – 10 ribs, a costal arch prosthesis (Figure 1B) was considering the surgically challenging implantation of
th
utilized rather than the in-suit rib prosthesis mainly the in-suit rib prosthesis, especially the great risk in the
because of the connection between these ribs with the fixation with the spine. The same method was used to
sternum is realized in the costal cartilage. Wire binding fix the vertical prosthesis with the ribs as the costal arch
was employed to fix the costal arch prosthesis with the prosthesis. The impact from the side of the body would
health rib; thus, through hole is necessary for the junctions. be the main threat to the mechanical safety of the vertical
The physical loading of the costal arch prosthesis in prosthesis. To simulate the mechanical performance of
the human body may mainly come from the accidental the prosthesis, a concentrated force of 200 N was loaded
impact; therefore, FEA was conducted to simulate the at the middle of the prosthesis in the FEA model, and
impact on the distal part of the costal arch prosthesis (red the result presented the maximum von Mises stress of
dashed circle in Figure 1B). The result showed that the approximately 30 MPa, which is much lower than the
226 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 4