Page 238 - IJB-8-4
P. 238
3DP PEEK implants for chest wall reconstruction
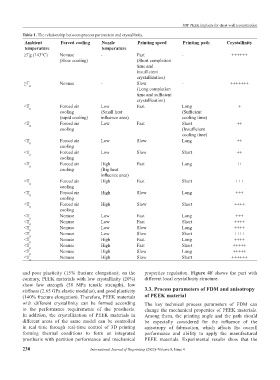
Table 1. The relationship between process parameters and crystallinity.
Ambient Forced cooling Nozzle Printing speed Printing path Crystallinity
temperature temperature
≥Tg (143℃) Nonuse - Fast - ++++++
(Slow cooling) (Short completion
time and
insufficient
crystallization)
≥T Nonuse - Slow - +++++++
g
(Long completion
time and sufficient
crystallization)
<T g Forced air Low Fast Long +
cooling (Small heat (Sufficient
(rapid cooling) influence area) cooling time)
<T g Forced air Low Fast Short ++
cooling (Insufficient
cooling time)
<T Forced air Low Slow Long ++
g
cooling
<T g Forced air Low Slow Short ++
cooling
<T Forced air High Fast Long ++
g
cooling (Big heat
influence area)
<T g Forced air High Fast Short +++
cooling
<T g Forced air High Slow Long +++
cooling
<T Forced air High Slow Short ++++
g
cooling
<T g Nonuse Low Fast Long +++
<T g Nonuse Low Fast Short ++++
<T g Nonuse Low Slow Long ++++
<T g Nonuse Low Slow Short ++++
<T g Nonuse High Fast Long ++++
<T g Nonuse High Fast Short +++++
<T g Nonuse High Slow Long +++++
<T g Nonuse High Slow Short ++++++
and poor plasticity (15% fracture elongation); on the properties regulation. Figure 4F shows the part with
contrary, PEEK materials with low crystallinity (20%) different local crystallinity structure.
show low strength (58 MPa tensile strength), low
stiffness (2.65 GPa elastic modulus), and good plasticity 3.3. Process parameters of FDM and anisotropy
(140% fracture elongation). Therefore, PEEK materials of PEEK material
with different crystallinity can be formed according The key technical process parameters of FDM can
to the performance requirements of the prosthesis. change the mechanical properties of PEEK materials.
In addition, the crystallization of PEEK materials in Among them, the printing angle and the path should
different areas of the same model can be controlled be especially considered for the influence of the
in real time through real-time control of 3D printing anisotropy of fabrication, which affects the overall
forming thermal conditions to form an integrated performance and ability to apply the manufactured
prosthesis with partition performance and mechanical PEEK materials. Experimental results show that the
230 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 4