Page 243 - IJB-8-4
P. 243
Wang, et al.
A B D
C E
F
H
G
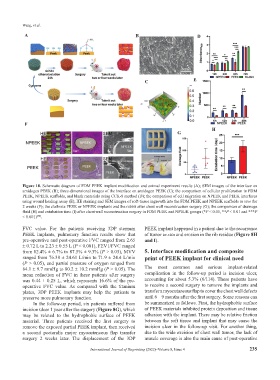
Figure 10. Schematic diagram of FDM PEEK implant modification and animal experiment results (A); SEM images of the interface on
amidogen PEEK (B); three-dimensional images of the interface on amidogen PEEK (C); the comparison of cellular proliferation in FDM
PEEK, NPEEK scaffolds, and blank materials using CCK-8 method (D); the comparison of cell migration on NPEEK and PEEK interfaces
using wound healing assay (E); HE staining and SEM images of soft-tissue ingrowth into the FDM PEEK and NPEEK scaffolds in vivo for
2 weeks (F); the clathrate PEEK or NPEEK implants and the rabbit after chest wall reconstruction surgery (G); the comparison of drainage
fluid (H) and extubation time (I) after chest wall reconstruction surgery in FDM PEEK and NPEEK groups (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P
< 0.001) .
[46]
FVC value. For the patients receiving 3DP sternum PEEK implant happened in a patient due to the recurrence
PEEK implants, pulmonary function results show that of tumor in situ and erosion in the rib residue (Figure 8H
pre-operative and post-operative FVC ranged from 2.65 and I).
± 0.72 L to 2.23 ± 0.55 L (P < 0.001), FEV1/FVC ranged
from 82.4% ± 6.7% to 87.5% ± 9.3% (P > 0.05), MVV 5. Interface modification and composite
ranged from 76.38 ± 24.61 L/min to 71.9 ± 24.4 L/min print of PEEK implant for clinical need
(P > 0.05), and partial pressure of oxygen ranged from
84.1 ± 9.7 mmHg to 80.2 ± 10.2 mmHg (P > 0.05). The The most common and serious implant-related
mean reduction of FVC in these patients after surgery complication in the follow-up period is incision ulcer,
was 0.44 ± 0.25 L, which represents 16.6% of the pre- accounting for about 5.3% (6/114). These patients have
operative FVC value. As compared with the titanium to receive a second surgery to remove the implants and
plates, 3DP PEEK implants may help the patients to transfer a myocutaneous flap to cover the chest wall defects
preserve more pulmonary function. until 6 – 9 months after the first surgery. Some reasons can
In the follow-up period, six patients suffered from be summarized as follows. First, the hydrophobic surface
incision ulcer 1 year after the surgery (Figure 8G), which of PEEK materials inhibited protein deposition and tissue
may be related to the hydrophobic surface of PEEK adhesion with the implant. There may be relative friction
material. Three patients received the first surgery to between the soft tissue and implant that may cause the
remove the exposed partial PEEK implant, then received incision ulcer in the follow-up visit. For another thing,
a second pectoralis major myocutaneous flap transfer due to the wide excision of chest wall tumor, the lack of
surgery 2 weeks later. The displacement of the 3DP muscle coverage is also the main cause of post-operative
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 4 235