Page 242 - IJB-8-4
P. 242
3DP PEEK implants for chest wall reconstruction
reserved in the connection of the implant for embracing implants for chest wall reconstruction. However, the
binding. Based on our experience, the 3DP PEEK implant mechanical property of titanium is much greater than
[72]
should be secured below the residual ribs to prevent the that of cortical bone or costicartilage . The motion of
implant from pushing against the skin and causing ulcers. thorax is restricted after using the titanium implants.
For the manubrium sterni and mesosternum implants, The forced vital capacity (FVC) of patients is reduced
we usually use eight titanium screws to fix the implant by more than 30% after traditional surgery [73-76] . The
with the residual sternum (Figure 8E and F). It is worth pulmonary function of patients decreased significantly if
mentioning that we always use two wires to bind the the mechanical mismatch implants were used in surgery.
implant with the clavicle. Although this fixation does not Thus, the FDM process with low crystallinity (≤25%)
restore motion of the sternoclavicular joint, it is stable was used in the middle segment of 3DP PEEK implant to
enough in the body during the following up period. make it flexible.
A pericardial patch was also suspended under the 3DP To test the effect of 3DP PEEK implant to pulmonary
PEEK implants to close the thorax. In our hospital, function, each patient received pulmonary function
65 patients received sternum reconstruction using 3DP examination before and after surgery. The pulmonary
PEEK implants, including 11 whole sternum implants, function of each patient was tested and compared
34 manubrium sterni, and 20 mesosternum implants. between pre-operative (1 week before the operation) and
The average weight of the 3DP PEEK sternum implant post-operative (3 months after the operation) groups.
was 107.4 ± 33.6 g. The main chest wall diseases were For the patients receiving 3DP ribs PEEK implants,
primary tumor and infection. The average chest wall pulmonary function results show that pre-operative
defect size was 140.9 ± 101.5 cm (range, 64– 900 cm ). and post-operative FVC ranged from 2.90 ± 0.66 L to
2
2
2.53 ± 0.80 L (P < 0.001), FEV1/FVC ranged from 82.4%
4.3. Pulmonary function assessment and adverse ± 5.7% to 81.8% ± 6.7% (P > 0.05), MVV ranged from
reactions of implants 83.73 ± 21.15 L/min to 83.19 ± 28.4 L/min (P < 0.49),
and partial pressure of oxygen ranged from 86.1
A healthy person breathes about 20 times/min. That ± 10.7 mmHg to 80.4 ± 9.2 mmHg (P > 0.05). The mean
is to say, and the thorax moves more than 10 million reduction of FVC in these patients after surgery was 0.36
times in 1 year. The titanium plates are the traditional ± 0.25 L, which represents 12.4% of the pre-operative
A B C
D
E F G
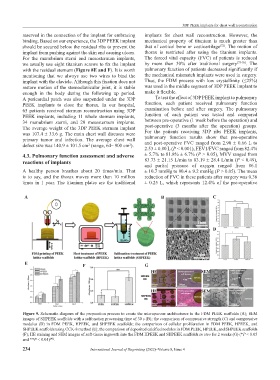
Figure 9. Schematic diagram of the preparation process to create the microporous architectures in the FDM PEEK scaffolds (A); SEM
images of SHPEEK scaffolds with a sulfonation processing time of 30 s (B); the comparison of compressive strength (C) and compressive
modulus (D) in FDM PEEK, HPEEK, and SHPEEK scaffolds; the comparison of cellular proliferation in FDM PEEK, HPEEK, and
SHPEEK scaffolds using CCK-8 method (E); the comparison of deposited calcified nodules in FDM PEEK, HPEEK, and SHPEEK scaffolds
(F); HE staining and SEM images of soft-tissue ingrowth into the FDM HPEEK and SHPEEK scaffolds in vivo for 2 weeks (G) (*P < 0.05
and **P < 0.01) .
[45]
234 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 4