Page 237 - IJB-8-4
P. 237
Wang, et al.
A B C
D E F
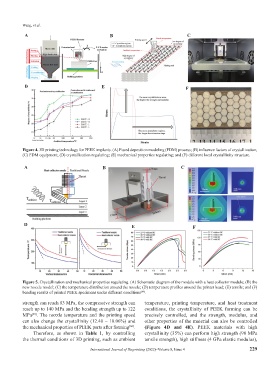
Figure 4. 3D printing technology for PEEK implants. (A) Fused deposition modeling (FDM) process; (B) influence factors of crystallization;
(C) FDM equipment; (D) crystallization regulating; (E) mechanical properties regulating; and (F) different local crystallinity structure.
A B C
D E F
Figure 5. Crystallization and mechanical properties regulating. (A) Schematic diagram of the module with a heat collector module; (B) the
new nozzle model; (C) the temperature distribution around the nozzle; (D) temperature profiles around the printer head; (E) tensile; and (F)
bending results of printed PEEK specimens under different conditions .
[68]
strength can reach 83 MPa, the compressive strength can temperature, printing temperature, and heat treatment
reach up to 140 MPa and the bending strength up to 122 conditions, the crystallinity of PEEK forming can be
MPa . The nozzle temperature and the printing speed precisely controlled, and the strength, modulus, and
[69]
can also change the crystallinity (12.40 – 18.06%) and other properties of the material can also be controlled
the mechanical properties of PEEK parts after forming . (Figure 4D and 4E). PEEK materials with high
[66]
Therefore, as shown in Table 1, by controlling crystallinity (35%) can perform high strength (90 MPa
the thermal conditions of 3D printing, such as ambient tensile strength), high stiffness (4 GPa elastic modulus),
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 4 229