Page 292 - IJB-8-4
P. 292
3D Printed Dressings for Burn Wound Treatment
and G4-A4 dressings. The lower free volume and higher to the ECM. Gelatin contains RGD peptide sequences,
entanglement are associated with higher consistency and which are essential for stable communication between the
flowability. It also justifies the lower viscosity and better cells and the surrounding ECM. The presence of amino
shape fidelity outputs in G4-A4 and G6-A2 dressings, acids and RGDs in the gelatin network provides favorable
which have the most entanglement between the gelatin anchors for cell attachment and proliferation to enhance
amide groups and alginate carboxylate/hydroxyl groups. cell adhesion through interactions with integrin and
These results collectively indicate the promising burn fibronectin [50,51] . On day 7, 3D-printed G6-A2 dressings
wound healing capacity of the G6-A2 dressing. showed higher cell viability than the control group and
other groups, which confirms the long-term cell viability
3.5. In vitro biological evaluation of the G6-A2 dressings.
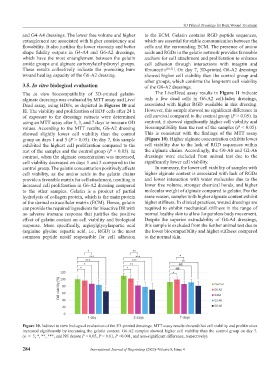
The in vitro biocompatibility of 3D-printed gelatin- The Live/Dead assay results in Figure 11 indicate
alginate dressings was evaluated by MTT assay and Live/ only a few dead cells in G6-A2 cell-laden dressings,
Dead assay, using HDFs, as depicted in Figures 10 and associated with higher RGD available in this dressing.
11. The viability and proliferation of HDF cells after 24 h However, this sample showed no significant difference in
of exposure to the dressings extracts were determined cell survival compared to the control group (P > 0.05). In
using an MTT assay after 1, 3, and 7 days to measure OD contrast, it showed significantly higher cell viability and
values. According to the MTT results, G6-A2 dressing biocompatibility than the rest of the samples (P < 0.05).
showed slightly lower cell viability than the control This is consistent with the findings of the MTT assay
group on days 1 and 3 (P > 0.05). On day 7, this sample (Figure 10). Higher alginate concentration exhibits lower
exhibited the highest cell proliferation compared to the cell viability due to the lack of RGD sequences within
rest of the samples and the control group (P < 0.05). In the alginate chains. Accordingly, the G0-A8 and G2-A6
contrast, when the alginate concentration was increased, dressings were excluded from animal test due to the
cell viability decreased on days 1 and 3 compared to the significantly lower cell viability.
control group. The gelatin concentration positively affects In summary, the lower cell viability of samples with
cell viability, as the amino acids in the gelatin chains higher alginate content is associated with lack of RGDs
provide a favorable matrix for cell attachment, resulting in and lower interaction with water molecules due to the
increased cell proliferation in G6-A2 dressing compared lower free volume, stronger chemical bonds, and higher
to the other samples. Gelatin is a product of partial molecular weight of alginate compared to gelatin. For the
hydrolysis of collagen protein, which is the main protein same reason, samples with higher alginate content exhibit
of the dermal extracellular matrix (ECM). Hence, gelatin higher stiffness. In clinical practices, wound dressings are
can provide the required ingredients for bioactive DR with required to exhibit mechanical stiffness in the range of
no adverse immune response that justifies the positive normal healthy skin to allow for painless body movement.
effect of gelatin content on cell viability and biological Despite the superior extrudability of G4-A4 dressings,
response. More specifically, arginylglycylaspartic acid this sample is excluded from the further animal test due to
(arginine–glycine–aspartic acid, i.e., RGD) is the most the lower biocompatibility and higher stiffness compared
common peptide motif responsible for cell adhesion to the normal skin.
Figure 10. Indirect in vitro biological evaluation of the 3D-printed dressings. MTT assay results showed that cell viability and proliferation
increased significantly by increasing the gelatin content. G6-A2 samples showed higher cell viability than the control group on day 7.
(n = 3; *, **, ***, and NS denote P < 0.05, P < 0.01, P <0.001, and non-significant difference, respectively).
284 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 4