Page 30 - IJB-8-4
P. 30
Xie, et al.
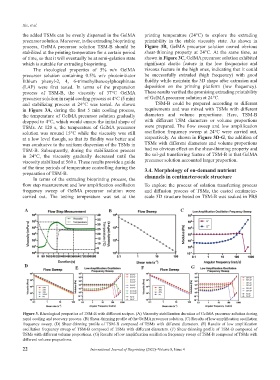
the added TSMs can be evenly dispersed in the GelMA printing temperature (24°C) to explore the extruding
precursor solution. Moreover, in the extruding bioprinting printability in the stable viscosity state. As shown in
process, GelMA precursor solution TSM-B should be Figure 3B, GelMA precursor solution owned obvious
stabilized at the printing temperature for a certain period shear-thinning property at 24°C. At the same time, as
of time, so that it will eventually be at semi-gelation state shown in Figure 3C, GelMA precursor solution exhibited
which is suitable for extruding bioprinting. significant elastic feature in the low frequencies and
The rheological properties of 5% w/v GelMA viscous feature in the high ones, indicating that it could
precursor solution containing 0.5% w/v photoinitiator be successfully extruded (high frequency) with good
lithium phenyl-2, 4, 6-trimethylbenzoylphosphinate fluidity while maintain the 3D shape after extrusion and
(LAP) were first tested. In terms of the preparation deposition on the printing platform (low frequency).
process of TSM-B, the viscosity of 37°C GelMA These results verified the promising extruding printability
precursor solution in rapid cooling process at 4°C (5 min) of GelMA precursor solution at 24°C.
and stabilizing process at 24°C was tested. As shown TSM-B could be prepared according to different
in Figure 3A, during the first 5 min cooling process, requirements and was mixed with TSMs with different
the temperature of GelMA precursor solution gradually diameters and volume proportions. Here, TSM-B
dropped to 4°C, which would ensure the initial shape of with different TSM diameters or volume proportions
TSMs. At 120 s, the temperature of GelMA precursor were prepared. The flow sweep and low amplification
solution was around 15°C while the viscosity was still oscillation frequency sweep at 24°C were carried out,
at a low level though, so that its fluidity was better and respectively. As shown in Figure 3D-G, the addition of
was conducive to the uniform dispersion of the TSMs in TSMs with different diameters and volume proportions
TSM-B. Subsequently, during the stabilization process had no obvious effect on the shear-thinning property and
in 24°C, the viscosity gradually decreased until the the sol-gel transferring feature of TSM-B in that GelMA
viscosity stabilized at 560 s. These results provide a guide precursor solution accounted larger proportion.
of the time periods of temperature controlling during the 3.4. Morphology of on-demand nutrient
preparation of TSM-B. channels in centimeter-scale structure
In terms of the extruding bioprinting process, the
flow step measurement and low amplification oscillation To explore the process of solation transferring process
frequency sweep of GelMA precursor solution were and diffusion process of TSMs, the casted centimeter-
carried out. The testing temperature was set at the scale 3D structure based on TSM-B was soaked in PBS
A B C
D E F G
Figure 3. Rheological properties of TSM-B with different recipes. (A) Viscosity stabilization duration of GelMA precursor solution during
rapid cooling and recovery process. (B) Shear-thinning profile of the GelMA precursor solution. (C) Results of low amplification oscillation
frequency sweep. (D) Shear-thinning profile of TSM-B composed of TSMs with different diameters. (E) Results of low amplification
oscillation frequency sweep of TSM-B composed of TSMs with different diameters. (F) Shear-thinning profile of TSM-B composed of
TSMs with different volume proportions. (G) Results of low amplification oscillation frequency sweep of TSM-B composed of TSMs with
different volume proportions.
22 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 4