Page 120 - IJB-9-2
P. 120
International Journal of Bioprinting Photocurable pullulan-based bioink for 3D printing
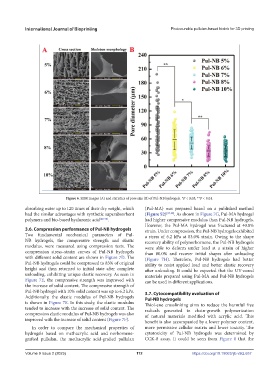
Figure 6. SEM images (A) and statistics of pore size (B) of Pul-NB hydrogels. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.
absorbing water up to 120 times of their dry weight, which (Pul-MA) was prepared based on a published method
had the similar advantages with synthetic superabsorbent (Figure S2) [37,38] . As shown in Figure 7G, Pul-MA hydrogel
polymers and bio-based hyaluronic acid [48-50] . had higher compressive modulus than Pul-NB hydrogels.
However, the Pul-MA hydrogel was fractured at 40.8%
3.6. Compression performance of Pul-NB hydrogels strain. Under compression, the Pul-NB hydrogels exhibited
Two fundamental mechanical parameters of Pul- a stress of 6.2 kPa at 83.0% strain. Owing to the shape
NB hydrogels, the compressive strength and elastic recovery ability of polynorbornene, the Pul-NB hydrogels
modulus, were measured using compression tests. The were able to deform under load at a strain of higher
compression stress–strain curves of Pul-NB hydrogels than 80.0% and recover initial shapes after unloading
with different solid content are shown in Figure 7D. The (Figure 7H). Therefore, Pul-NB hydrogels had better
Pul-NB hydrogels could be compressed to 83% of original ability to resist applied load and better elastic recovery
height and then returned to initial state after complete after unloading. It could be expected that the UV-cured
unloading, exhibiting unique elastic recovery. As seen in materials prepared using Pul-MA and Pul-NB hydrogels
Figure 7E, the compressive strength was improved with can be used in different applications.
the increase of solid content. The compressive strength of
Pul-NB hydrogel with 10% solid content was up to 6.2 kPa. 3.7. Cytocompatibility evaluation of
Additionally, the elastic modulus of Pul-NB hydrogels Pul-NB hydrogels
is shown in Figure 7E. In this study, the elastic modulus Thiol-ene crosslinking aims to reduce the harmful free
tended to increase with the increase of solid content. The radicals generated in chain-growth polymerization
compression elastic modulus of Pul-NB hydrogels was also of natural materials modified with acrylic acid. This
improved with the increase of solid content (Figure 7F). benefit is also accompanied by a lower polymer content,
In order to compare the mechanical properties of more permissive cellular matrix and lower toxicity. The
hydrogels based on methacrylic acid and norbornene- cytotoxicity of Pul-NB hydrogels was determined by
grafted pullulan, the methacrylic acid-grafted pullulan CCK-8 assay. It could be seen from Figure 8 that the
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 112 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.657