Page 343 - IJB-9-2
P. 343
International Journal of Bioprinting Characterization of BITC antibacterial hydrogel
A B
C D
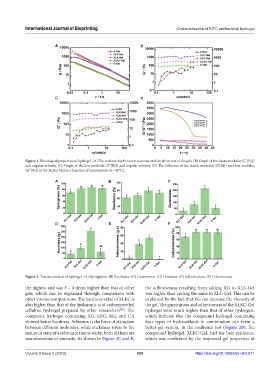
Figure 1. Rheological properties of hydrogel. (A) The relationship between viscosity and the shear rate of the gels. (B) Graph of the elastic modulus (G’[Pa])
and angular velocity. (C) Graph of the loss modulus (G’’[Pa]) and angular velocity. (D) The influence of the elastic modulus (G’[Pa]) and loss modulus
(G’’[Pa]) of the XLKC-Gel as a function of temperature (4 – 40°C).
A B C
D E F
Figure 2. Texture analysis of hydrogel. (A) Springiness. (B) Resilience. (C) Gumminess. (D) Hardness. (E) Adhesiveness. (F) Cohesiveness.
the highest and was 3 – 4 times higher than that of other the adhesiveness resulting from adding KG to XLK-Gel
gels, which can be explained through comparison with was higher than adding the same to XLC-Gel. This can be
other viscose compositions. The hardness value of XLKC is explained by the fact that KG can increase the viscosity of
also higher than that of the hyaluronic acid carboxymethyl the gel. The gumminess and adhesiveness of the XLKC-Gel
cellulose hydrogel prepared by other researchers . The hydrogel were much higher than that of other hydrogels,
[33]
composite hydrogel containing XG, LBG, KG, and CA which indicate that the compound hydrogel containing
showed better hardness. Adhesion is the force of attraction four types of hydrocolloids in combination can form a
between different molecules, while stickiness refers to the better gel system. In the resilience test (Figure 2B), the
nature or state of a substance that is sticky; both of them are compound hydrogel, XLKC-Gel, had the best resilience,
manifestations of viscosity. As shown in Figure 2C and E, which was confirmed by the improved gel properties of
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 335 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.671