Page 399 - IJB-9-2
P. 399
International Journal of Bioprinting In situ 3D bioprinter for skin wound healing
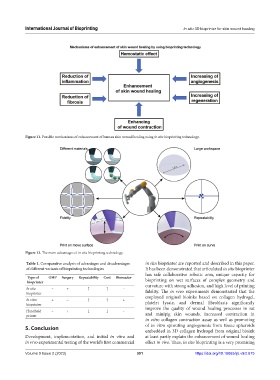
Figure 11. Possible mechanisms of enhancement of human skin wound healing using in situ bioprinting technology.
Figure 12. The main advantages of in situ bioprinting technology.
Table 1. Comparative analysis of advantages and disadvantages in situ bioprinter are reported and described in this paper.
of different variants of bioprinting technologies It has been demonstrated that articulated in situ bioprinter
has safe collaborative robotic arm, unique capacity for
Type of GMP Surgery Repeatability Cost Bioreactor
bioprinter bioprinting on wet surfaces of complex geometry and
In situ – + ↑ ↑ - curvature with strong adhesion, and high level of printing
bioprinter fidelity. The in vivo experiments demonstrated that the
In vitro + – ↑ ↑ + employed original bioinks based on collagen hydrogel,
bioprinter platelet lysate, and dermal fibroblasts significantly
Handheld – + ↓ ↓ - improve the quality of wound healing processes in rat
printer and minipig skin wounds. Increased contraction in
in vitro collagen contraction assay as well as promoting
5. Conclusion of in vitro sprouting angiogenesis from tissue spheroids
embedded in 3D collagen hydrogel from original bioink
Development, implementation, and initial in vitro and at least partly explain the enhancement of wound healing
in vivo experimental testing of the world’s first commercial effect in vivo. Thus, in situ bioprinting is a very promising
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 391 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.675