Page 64 - IJB-9-2
P. 64
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinting in wound dressing and healing
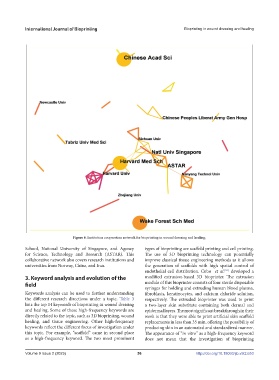
Figure 6. Institution cooperation network for bioprinting in wound dressing and healing.
School, National University of Singapore, and Agency types of bioprinting are scaffold printing and cell printing.
for Science, Technology and Research (ASTAR). This The use of 3D bioprinting technology can potentially
collaborative network also covers research institutions and improve classical tissue engineering methods as it allows
universities from Norway, China, and Iran. the generation of scaffolds with high spatial control of
[51]
endothelial cell distribution. Cubo et al. developed a
3. Keyword analysis and evolution of the modified extrusion-based 3D bioprinter. The extrusion
field module of this bioprinter consists of four sterile disposable
syringes for holding and extruding human blood plasma,
Keywords analysis can be used to further understanding fibroblasts, keratinocytes, and calcium chloride solution,
the different research directions under a topic. Table 3 respectively. The extruded bioprinter was used to print
lists the top 14 keywords of bioprinting in wound dressing a two-layer skin substitute containing both dermal and
and healing. Some of these high-frequency keywords are epidermal layers. The most significant breakthrough in their
directly related to the topic, such as 3D bioprinting, wound work is that they were able to print artificial skin scaffold
healing, and tissue engineering. Other high-frequency replacements in less than 35 min, offering the possibility of
keywords reflect the different focus of investigation under producing skin in an automated and standardized manner.
this topic. For example, “scaffold” came in second place The appearance of “in vitro” as a high-frequency keyword
as a high-frequency keyword. The two most prominent does not mean that the investigation of bioprinting
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 56 http://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.653