Page 66 - IJB-9-2
P. 66
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinting in wound dressing and healing
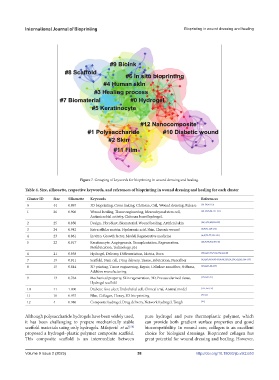
Figure 7. Grouping of keywords for bioprinting in wound dressing and healing.
Table 4. Size, silhouette, respective keywords, and references of bioprinting in wound dressing and healing for each cluster
Cluster ID Size Silhouette Keywords References
0 44 0.897 3D bioprinting, Cross linking, Chitosan, Cell, Wound dressing, Release [56-59,96-112]
1 26 0.906 Wound healing, Tissue engineering, Mesenchymal stem cell, [60-64,95,98,113-121]
Antimicrobial activity, Chitosan based hydrogel,
2 25 0.850 Design, Fibroblast, Biomaterial, Wound healing, Artificial skin [24,51,75,80,122-127]
3 24 0.942 Extracellular matrix, Hyaluronic acid, Skin, Chronic wound [6,70,71,128-134]
4 23 0.861 In vitro, Growth factor, Model, Regenerative medicine [6,47,72-77,135-139]
5 22 0.917 Keratinocyte, Angiogenesis, Transplantation, Regeneration, [26,76,78,96,140-143]
Biofabrication, Technology, pH
6 21 0.938 Hydrogel, Delivery, Differentiation, Matrix, Burn [50,52,67,77,79-82,99,144-146]
7 19 0.911 Scaffold, Stem cell, Drug delivery, Tissue, Fabrication, Nanofiber [6,24,47,56,58,83-85,96,98,115,124,136,141,142,146-155]
8 15 0.844 3D printing, Tissue engineering, Repair, Cellulose nanofiber, Stiffness, [25,82,86-88,145]
Additive manufacturing
9 13 0.764 Mechanical property, Skin regeneration, 3D, Prevascularized tissue, [27,83,89-91]
Hydrogel scaffold
10 11 1.000 Diabetic foot ulcer, Endothelial cell, Clinical trial, Animal model [135,156,157]
11 10 0.957 Film, Collagen, Honey, 3D bio-printing [93,94]
12 4 0.986 Composite hydrogel, Drug delivery, Network hydrogel, Tough [95]
Although polysaccharide hydrogels have been widely used, pure hydrogel and pure thermoplastic polymer, which
it has been challenging to prepare mechanically stable can provide both gradient surface properties and good
scaffold materials using only hydrogels. Milojević et al. biocompatibility. In wound care, collagen is an excellent
[58]
proposed a hydrogel–plastic polymer composite scaffold. choice for biological dressings. Bioprinted collagen has
This composite scaffold is an intermediate between great potential for wound dressing and healing. However,
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 58 http://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.653