Page 104 - IJB-9-3
P. 104
International Journal of Bioprinting The biological properties of WE43 scaffolds via the oxidative heat strategy
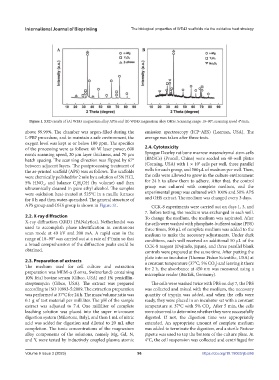
Figure 1. XRD results of (A) WE43 magnesium alloy APSs and (B) WE43 magnesium alloy OHSs. Scanning range: 10–90°; scanning speed 4°/min.
above 99.99%. The chamber was argon-filled during the emission spectroscopy (ICP‒AES) (Leeman, USA). The
L-PBF procedure, and to maintain a safe environment, the average was taken after three tests.
oxygen level was kept at or below 100 ppm. The specifics
of the processing were as follows: 60 W laser power, 600 2.4. Cytotoxicity
mm/s scanning speed, 20 μm layer thickness, and 70 μm Sprague Dawley rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
hatch spacing. The scanning direction was flipped by 67° (BMSCs) (Procell, China) were seeded on 48-well plates
4
between adjacent layers. The postprocessing treatment of (Corning, USA) with 1 × 10 cells per well, three parallel
the as-printed scaffold (APS) was as follows. The scaffolds wells for each group, and 500 μL of medium per well. Then,
were chemically polished for 2 min by a solution of 5% HCl, the cells were allowed to grow in the culture environment
5% HNO , and balance C H OH (by volume) and then for 24 h to allow them to adhere. After that, the control
3
2
5
ultrasonically cleaned in pure ethyl alcohol. The samples group was cultured with complete medium, and the
were oxidation heat-treated at 525°C in a muffle furnace experimental group was cultured with 100% and 50% APS
for 8 h and then water-quenched. The general structure of and OHS extract. The medium was changed every 3 days.
APS group and OHS group is shown in Figure S1. CCK-8 experiments were carried out on days 1, 3, and
7. Before testing, the medium was exchanged in each well.
2.2. X-ray diffraction To change the medium, the medium was aspirated. After
X-ray diffraction (XRD) (PANalytical, Netherlands) was the cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)
used to accomplish phase identification in continuous three times, 500 μL of complete medium was added to the
scan mode at 40 kV and 200 mA. A rapid scan in the medium to make the necessary adjustments. Under dark
range of 10–90° was carried out at a rate of 4°/min so that conditions, each well received an additional 50 μL of the
a broad comprehension of the diffraction peaks could be CCK-8 reagent (Dojindo, Japan), and three parallel blank
obtained. controls were prepared at the same time. After putting the
plate into an incubator (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) at
2.3. Preparation of extracts a constant temperature (37°C, 5% CO ) and leaving it there
2
The medium used for cell culture and extraction for 2 h, the absorbance at 450 nm was measured using a
preparation was MEM-α (Lonza, Switzerland) containing microplate reader (BioTek, Germany).
10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco, USA) and 1% penicillin-
streptomycin (Gibco, USA). The extract was prepared The cells were washed twice with PBS on day 7, the PBS
according to ISO 10993-5:2009. The extraction preparation was collected and mixed with the medium, the necessary
was performed at 37°C for 24 h. The mass/volume ratio was quantity of trypsin was added, and when the cells were
0.1 g of test material per milliliter. The pH of the sample ready, they were placed in an incubator set with a constant
extract was adjusted to 7.4. One milliliter of complete temperature at 37°C with 5% CO . After 5 min, the cells
2
leaching solution was placed into the super microwave were observed to determine whether they were successfully
digestion system (Milestone, Italy), and then 1 mL of nitric digested. If not, the digestion time was appropriately
acid was added for digestion and diluted to 20 mL after extended. An appropriate amount of complete medium
completion. The ionic concentrations of the magnesium was added to terminate the digestion, and a sterile Pasteur
alloy components of the solutions, namely Mg, Gd, N, pipette was used to tap the bottom of the culture plate. At
and Y, were tested by inductively coupled plasma atomic 4°C, the cell suspension was collected and centrifuged for
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 96 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.686