Page 108 - IJB-9-3
P. 108
International Journal of Bioprinting The biological properties of WE43 scaffolds via the oxidative heat strategy
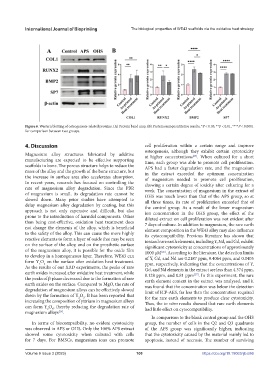
Figure 6. Western blotting of osteogenesis-related proteins. (A) Protein band map. (B) Protein semiquantitative results. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001
for comparison between two groups.
4. Discussion cell proliferation within a certain range and improve
osteogenesis, although they exhibit certain cytotoxicity
Magnesium alloy structures fabricated by additive at higher concentrations . When cultured for a short
[25]
manufacturing are expected to be effective supporting time, each group was able to promote cell proliferation.
scaffolds in bone. The porous structure helps to reduce the APS had a faster degradation rate, and the magnesium
mass of the alloy and the growth of the bone structure, but in the extract exceeded the optimum concentration
the increase in surface area also accelerates absorption. of magnesium needed to promote cell proliferation,
In recent years, research has focused on controlling the showing a certain degree of toxicity after culturing for a
rate of magnesium alloy degradation. Since the PBR week. The concentration of magnesium in the extract of
of magnesium is small, its degradation rate cannot be OHS was much lower than that of the APS group, so at
slowed down. Many prior studies have attempted to all three times, its rate of proliferation exceeded that of
delay magnesium alloy degradation by coating, but this the control group. As a result of the lower magnesium
approach is not only expensive and difficult, but also ion concentration in the OHS group, the effect of the
prone to the introduction of harmful components. Other diluted extract on cell proliferation was not evident after
than being cost-effective, oxidation heat treatment does 7 days of culture. In addition to magnesium, the rare earth
not change the elements of the alloy, which is beneficial element composition in the WE43 alloy may also influence
to the safety of the alloy. This can cause the more highly its cytocompatibility. Previous literature has shown that
reactive elements to form a layer of oxide that may be seen ionized rare earth elements, including Y, Nd, and Gd, exhibit
on the surface of the alloy, and on the prosthetic surface significant cytotoxicity at concentrations of approximately
of the magnesium alloy, it is possible for the oxide film 1000 μM . According to the literature, the detection limits
[26]
to develop in a homogeneous layer. Therefore, WE43 can of Y, Gd, and Nd are 0.2187 ppm, 0.4064 ppm, and 0.0405
form Y O on the surface after oxidation heat treatment. ppm, respectively, indicating that the concentrations of Y,
2
3
As the results of our XRD experiments, the peaks of rare Gd, and Nd elements in the extract are less than 4.374 ppm,
earth oxides increased after oxidative heat treatment, while 8.128 ppm, and 0.81 ppm . In this experiment, the rare
[27]
the peaks of β phase decreased due to the formation of rare earth element content in the extract was analyzed, and it
earth oxides on the surface. Compared to MgO, the rate of was found that the concentration was below the detection
degradation of magnesium alloys can be effectively slowed limit of ICP-AES, far less than the concentration required
down by the formation of Y O . It has been reported that for the rare earth elements to produce clear cytotoxicity.
2
3
increasing the composition of yttrium in magnesium alloys Thus, the in vitro results showed that rare earth elements
can form Y O , thereby reducing the degradation rate of had little effect on cytocompatibility.
3
2
magnesium alloys .
[24]
In comparison to the blank control group and the OHS
In terms of biocompatibility, no evident cytotoxicity group, the number of cells in the Q2 and Q3 quadrants
was observed in APS or OHS. Only the 100% APS extract of the APS group was significantly higher, indicating
showed some cytotoxicity when cultured with cells that the cytotoxicity caused by the material mainly led to
for 7 days. For BMSCs, magnesium ions can promote apoptosis, instead of necrosis. The number of surviving
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 100 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.686