Page 134 - IJB-9-3
P. 134
International Journal of Bioprinting Programmable formaldehyde dehydrogenase for biodegradation formaldehyde
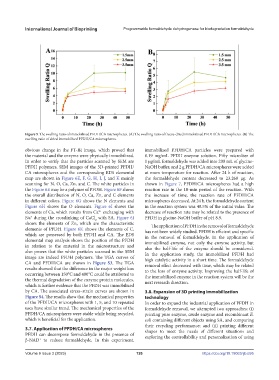
Figure 5. The swelling ratio of immobilized PFDH/CA microspheres. (A) The swelling ratio of freeze-dried immobilized PFDH/CA microspheres. (B) The
swelling ratio of dried immobilized PFDH/CA microspheres.
obvious change in the FT-IR image, which proved that immobilized PFDH/CA particles were prepared with
the material and the enzyme were physically immobilized. 0.19 mg/mL PFDH enzyme solution. Fifty microliter of
In order to verify that the particles scanned by SEM are 1 µg/mL formaldehyde was added into 200 mL of glycine-
PFDH polymers, SEM images of the 3D-printed PFDH/ NaOH buffer, and 2 g PFDH/CA microspheres were added
CA microspheres and the corresponding EDS elemental at room temperature for reaction. After 24 h of reaction,
map are shown in Figure 6E, F, G, H, I, J, and K mainly the formaldehyde content decreased to 23.268 μg. As
scanning for N, O, Ca, Zn, and C. The white particles in shown in Figure 7, PFDH/CA microspheres had a high
the Figure 6E may be a polymer of PFDH. Figure 6F shows reaction rate in the 10-min period of the reaction. With
the overall distribution of N, O, Ca, Zn, and C elements the increase of time, the reaction rate of PFDH/CA
in different colors. Figure 6G shows the N elements and microspheres decreased. At 24 h, the formaldehyde content
Figure 6H shows the O elements. Figure 6I shows the in the reaction system was 48.5% of the initial value. The
elements of Ca, which results from Ca exchanging with decrease of reaction rate may be related to the presence of
2+
Na during the crosslinking of CaCl with SA. Figure 6J PFDH in glycine-NaOH buffer of pH 8.9.
+
2
shows the elements of Zn, which are the characteristic The application of PFDH in the removal of formaldehyde
elements of PFDH. Figure 6K shows the elements of C, has not been widely studied. PFDH is efficient and specific
which are possessed by both PFDH and CA. The EDS in the removal of formaldehyde. In the application of
elemental map analysis shows the position of the PFDH immobilized enzyme, not only the enzyme activity, but
in relation to the material in the microstructure and also the half-life of the enzyme should be considered.
also proves that the white particles scanned in the SEM In the application study, the immobilized PFDH had
image are indeed PFDH polymers. The TGA curves of high catalytic activity in a short time. The formaldehyde
CA and PFDH/CA are shown in Figure S3. The TGA removal effect decreased with time, which may be related
results showed that the difference in the major weight loss to the loss of enzyme activity. Improving the half-life of
occurring between 150°C and 480°C could be attributed to the immobilized enzyme in the reaction system will be the
the thermal degradation of the enzyme protein molecules, next research direction.
which is further evidence that the PFDH was immobilized
by CA. The associated stress–strain curves are shown in 3.8. Expansion of 3D printing immobilization
Figure S4. The results show that the mechanical properties technology
of the PFDH/CA microspheres with 1, 5, and 10 repeated In order to expand the industrial application of PFDH in
uses have similar trend. The mechanical properties of the formaldehyde removal, we attempted two approaches: (i)
PFDH/CA microspheres were stable while being recycled, printing pure enzyme, crude enzyme and recombinant E.
which is beneficial for the application. coli containing different objects using SA, and comparing
their recycling performance; and (ii) printing different
3.7. Application of PFDH/CA microspheres shapes to meet the needs of different situations and
PFDH can decompose formaldehyde in the presence of exploring the controllability and personalization of using
β-NAD to reduce formaldehyde. In this experiment,
+
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 126 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.695