Page 161 - IJB-9-3
P. 161
International Journal of Bioprinting LPBF of AKM/PEEK biological composite
Table 4. Mechanical properties of PEEK and its composites.
Materials Fracture elongation (%) Yield strength (MPa) Tensile strength (MPa) Young’s modulus (MPa)
Pure PEEK 6.91 ± 0.95 55.90 ± 5.19 98.74 ± 0.48 3706.00 ± 114.13
5 wt% AKM/PEEK 3.09 ± 0.16 58.30 ± 1.61 69.53 ± 2.64 3090.82 ± 92.56
10 wt% AKM/PEEK 2.65 ± 0.11 33.20 ± 1.69 40.28 ± 0.36 2221.55 ± 25.17
15 wt% AKM/PEEK 1.93 ± 0.13 25.10 ± 1.23 30.83 ± 0.46 2269.48 ± 81.67
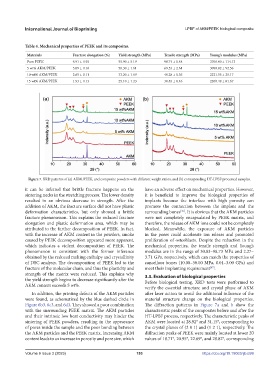
Figure 7. XRD patterns of (a) AKM, PEEK, and composite powders with different weight ratios, and (b) corresponding HT-LPBF processed samples.
it can be inferred that brittle fracture happens on the have an adverse effect on mechanical properties. However,
sintering necks in the stretching process. The lower density it is beneficial to improve the biological properties of
resulted in an obvious decrease in strength. After the implants because the interface with high porosity can
addition of AKM, the fracture surface did not have plastic promote the connection between the implant and the
deformation characteristics, but only showed a brittle surrounding bones . It is obvious that the AKM particles
[46]
fracture phenomenon. This explains the reduced fracture were not completely encapsulated by PEEK matrix, and
elongation and plastic deformation area, which may be therefore, the release of AKM ions could not be completely
attributed to the further decomposition of PEEK. In fact, blocked. Meanwhile, the exposure of AKM particles
with the increase of AKM content in the powders, smoke in the pores could accelerate ion release and promoted
caused by PEEK decomposition appeared more apparent, proliferation of osteoblasts. Despite the reduction in the
which indicates a violent decomposition of PEEK. The mechanical properties, the tensile strength and Young’s
phenomenon is consistent with the former inference modulus are in the range of 30.83–98.73 MPa and 2.27–
obtained by the reduced melting enthalpy and crystallinity 3.71 GPa, respectively, which can match the properties of
of DSC analysis. The decomposition of PEEK led to the cancellous bones (10.00–50.00 MPa, 0.01–3.00 GPa) and
fracture of the molecular chain, and thus the plasticity and meet their implanting requirement .
[47]
strength of the matrix were reduced. This explains why 3.3. Evaluation of biological properties
the yield strength begins to decrease significantly after the Before biological testing, XRD tests were performed to
AKM content exceeds 5 wt%.
verify the essential structure and crystal phase of AKM
In addition, the printing defects of the AKM particles after laser action to avoid the additional influence of the
were found, as schematized by the blue dashed circle in material structure change on the biological properties.
Figure 6b3, 6c3, and 6d3. They showed a poor combination The diffraction patterns in Figure 7a and b show the
with the surrounding PEEK matrix. The AKM particles characteristic peaks of the composites before and after the
and their intrinsic low heat conductivity may hinder the HT-LPBF process, respectively. The characteristic peaks of
sintering of PEEK powders, resulting in the appearance AKM were located at 28.92° and 31.15°, corresponding to
of pores inside the sample and the poor bonding between the crystal planes of (2 0 1) and (1 2 1), respectively. The
the AKM particles and the PEEK matrix. Increasing AKM diffraction peaks of PEEK were mainly located at lower 2θ
content leads to an increase in porosity and pore size, which values of 18.71°, 20.95°, 22.69°, and 28.82°, corresponding
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 153 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.699