Page 164 - IJB-9-3
P. 164
International Journal of Bioprinting LPBF of AKM/PEEK biological composite
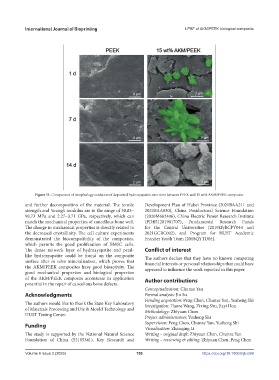
Figure 11. Comparison of morphology evolution of deposited hydroxyapatite over time between PEEK and 15 wt% AKM/PEEK composite.
and further decomposition of the material. The tensile Development Plan of Hubei Province (2021BAA211 and
strength and Young’s modulus are in the range of 30.83– 2022BAA030), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
98.73 MPa and 2.27–3.71 GPa, respectively, which can (2020M682406), China Electric Power Research Institute
match the mechanical properties of cancellous bone well. (PDB51201901707), Fundamental Research Funds
The change in mechanical properties is directly related to for the Central Universities (2019kfyRCPY044 and
the decreased crystallinity. The cell culture experiments 2021GCRC002), and Program for HUST Academic
demonstrated the biocompatibility of the composites, Frontier Youth Team (2018QYTD04).
which permits the good proliferation of BMSC cells.
The dense network layer of hydroxyapatite and petal- Conflict of interest
like hydroxyapatite could be found on the composite The authors declare that they have no known competing
surface after in vitro mineralization, which proves that financial interests or personal relationships that could have
the AKM/PEEK composites have good bioactivity. The appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
good mechanical properties and biological properties
of the AKM/PEEK composite accentuate its application Author contributions
potential in the repair of cancellous bone defects.
Conceptualization: Chunze Yan
Acknowledgments Formal analysis: Jin Su
Funding acquisition: Peng Chen, Chunze Yan, Yusheng Shi
The authors would like to thank the State Key Laboratory Investigation: Haoze Wang, Zixing Shu, Jiayi Hou
of Materials Processing and Die & Mould Technology and Methodology: Zhiyuan Chen
HUST Testing Center. Project administration: Yusheng Shi
Funding Supervision: Peng Chen, Chunze Yan, Yusheng Shi
Visualization: Zhaoqing Li
The study is supported by the National Natural Science Writing – original draft: Zhiyuan Chen, Chunze Yan
Foundation of China (52105341), Key Research and Writing – reviewing & editing: Zhiyuan Chen, Peng Chen
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 156 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.699