Page 235 - IJB-9-3
P. 235
International Journal of Bioprinting Biomaterials for vascularized and innervated tissue regeneration
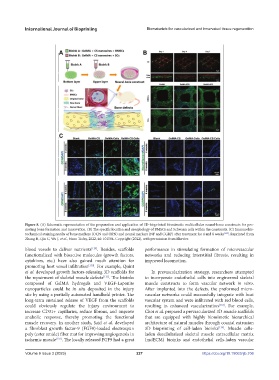
Figure 8. (A) Schematic representation of the preparation and application of 3D-bioprinted biomimetic multicellular neural-bone constructs for pro-
moting bone formation and innervation. (B) The specific location and morphology of BMSCs and Schwann cells within the constructs. (C) Immunohis-
tochemical staining results of bone markers (OCN and OPN) and neural markers (NF and CGRP) after treatment for 4 and 8 weeks [125] . Reprinted from
Zhang H, Qin C, Wu J, et al., Nano Today, 2022, 46: 101584. Copyright (2022), with permission from Elsevier.
blood vessels to deliver nutrients [129] . Besides, scaffolds performance in stimulating formation of microvascular
functionalized with bioactive molecules (growth factors, networks and reducing interstitial fibrosis, resulting in
cytokines, etc.) have also gained much attention for improved locomotion.
promoting host vessel infiltration [130] . For example, Quint
et al. developed growth factors-releasing 3D scaffolds for In prevascularization strategy, researchers attempted
the repairment of skeletal muscle defects [131] . The bioinks to incorporate endothelial cells into engineered skeletal
composed of GelMA hydrogels and VEGF-Laponite muscle constructs to form vascular network in vitro.
nanoparticles could be in situ deposited in the injury After implanted into the defects, the preformed micro-
site by using a partially automated handheld printer. The vascular networks could successfully integrate with host
long-term sustained release of VEGF from the scaffolds vascular system and were infiltrated with red blood cells,
could obviously regulate the injury environment to resulting in enhanced vascularization [133] . For example,
increase CD31+ capillaries, reduce fibrous, and improve Choi et al. prepared a prevascularized 3D muscle scaffolds
anabolic response, thereby promoting the functional that are equipped with highly biomimetic hierarchical
muscle recovery. In another study, Said et al. developed architecture of natural muscles through coaxial extrusion
a fibroblast growth factor-9 (FGF9)-loaded electrospun 3D bioprinting of cell-laden bioinks [134] . Muscle cells-
poly (ester amide) fiber mat for improving angiogenesis in laden decellularized skeletal muscle extracellular matrix
ischemic muscle [132] . The locally released FGF9 had a great (mdECM) bioinks and endothelial cells-laden vascular
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 227 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.706