Page 237 - IJB-9-3
P. 237
International Journal of Bioprinting Biomaterials for vascularized and innervated tissue regeneration
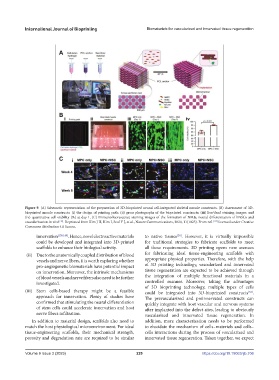
Figure 9. (A) Schematic representation of the preparation of 3D-bioprinted neural cell-integrated skeletal muscle constructs. (B) Assessment of 3D-
bioprinted muscle constructs: (i) the design of printing path; (ii) gross photographs of the bioprinted constructs; (iii) live/dead staining images; and
(iv) quantitative cell viability (%) at day 1. (C) Immunofluorescence staining images of the formation of NMJs, neural differentiation of hNSCs and
vascularization in vivo [139] . Reprinted from Kim J H, Kim I, Seol Y J, et al., Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1025). From ref. [139] licensed under Creative
Commons Attribution 4.0 license.
innervation [128,140] . Hence, novel electroactive materials to native tissues . However, it is virtually impossible
[20]
could be developed and integrated into 3D-printed for traditional strategies to fabricate scaffolds to meet
scaffolds to enhance their biological activity. all these requirements. 3D printing opens new avenues
(ii) Due to the anatomically coupled distribution of blood for fabricating ideal tissue-engineering scaffolds with
vessels and nerve fibers, it is worth exploring whether appropriate physical properties. Therefore, with the help
pro-angiogenetic biomaterials have potential impact of 3D printing technology, vascularized and innervated
on innervation. Moreover, the intrinsic mechanisms tissue regeneration are expected to be achieved through
of blood vessels and nerve fibers also need to be further the integration of multiple functional materials in a
investigated. controlled manner. Moreover, taking the advantages
of 3D bioprinting technology, multiple types of cells
(iii) Stem cells-based therapy might be a feasible could be integrated into 3D-bioprinted constructs .
[52]
approach for innervation. Plenty of studies have The prevascularized and preinnervated constructs can
confirmed that stimulating the neural differentiation quickly integrate with host vascular and nervous systems
of stem cells could accelerate innervation and host after implanted into the defect sites, leading to obviously
nerve fibers infiltration. vascularized and innervated tissue regeneration. In
In addition to material design, scaffolds also need to addition, more characterization needs to be performed
match the host physiological microenvironment. For ideal to elucidate the mechanism of cells–materials and cells–
tissue-engineering scaffolds, their mechanical strength, cells interactions during the process of vascularized and
porosity and degradation rate are required to be similar innervated tissue regeneration. Taken together, we expect
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 229 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.706