Page 294 - IJB-9-3
P. 294
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting as a prospective therapeutic strategy for LSCD
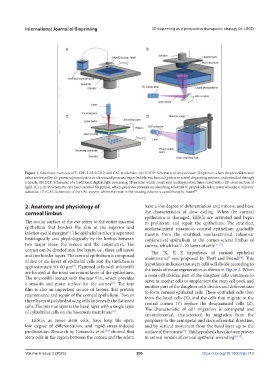
Figure 1. Schematic overview of E‐3DP, L-3DP, DLP, and CAL modalities. (A) E‐3DP: Schematic of an extrusion 3D‐printer, where droplets/filaments/
tubes are forced by air-pressure/piezoelectric or ultrasound pressure/vapor bubble/mechanical (piston or screw) dispensing systems, and extruded through
a nozzle. (B) DLP: Schematic of a traditional digital‐light‐processing 3D printer, which constructs multilayer structures cured with a 2D cross‐section of
light. (C) L-3DP: Schematic of a laser-assisted 3D printer, which generates pressure on absorbing substrate to propel cell–laden materials onto a collector
substrate. (D) CAL: Schematic of the CAL system, where the resin in the rotating volume is cured frame by frame .
[5]
2. Anatomy and physiology of have a low degree of differentiation and mitosis, and have
corneal limbus the characteristics of slow cycling. When the corneal
epithelium is damaged, LESCs are activated and begin
The ocular surface of the eye refers to the entire mucosal to proliferate and repair the epithelium. The stratified,
epithelium that borders the skin at the superior and nonkeratinized squamous corneal epithelium gradually
inferior eyelid margins . The epithelial surface is separated transits from the stratified, nonkeratinized columnar
[6]
histologically and physiologically by the limbus between conjunctival epithelium at the cornea-scleral limbus of
two major areas: the cornea and the conjunctiva. The cornea, which has 7–10 layers of cells [11-13] .
cornea can be divided into five layers, i.e., three cell layers The “X, Y, Z hypothesis of corneal epithelial
and two border layers. The corneal epithelium is composed maintenance” was proposed by Thoft and Friend . This
[14]
of five or six layers of epithelial cells and the thickness is hypothesis indicates that stem cells will divide according to
approximately 50–60 μm . Flattened cells with microvilli the needs of tissue regeneration as shown in Figure 2. When
[7]
are located at the most outermost layer of the epithelium. a stem cell divides, part of the daughter cells continues to
The microvilli interact with the tear film, which provides serve as mother cells to supplement the stem cell pool, and
a smooth and moist surface for the cornea . The tear another part of the daughter cells divides and differentiates
[8]
film is also an important source of factors that provide to form corneal epithelial cells. These epithelial cells then
maintenance and repair of the corneal epithelium. Two or form the basal cells (X), and the cells that migrate to the
three layers of polyhedral wing cells lie beneath the flattened central cornea (Y) replace the desquamated cells (Z).
cells. The internal layer is the basal layer with a single layer The characteristic of cell migration is centripetal and
of cylindrical cells on the basement membrane .
[9]
circumferential, characterized by migration from the
LESCs, as tissue stem cells, have long life span, periphery to the centripetal and circumferential direction,
low degree of differentiation, and rapid stress-induced and by vertical movement from the basal layer up to the
proliferation. Research by Cotsarelis et al. showed that surface of the cornea . This hypothesis has also been proven
[10]
[15]
stem cells in the region between the cornea and the sclera in animal models of corneal epithelial wounding [16,17] .
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 286 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.710