Page 440 - IJB-9-3
P. 440
International Journal of Bioprinting Gelatin-PVA crosslinked genipin bioinks for skin tissue engineering
there were no significant changes in the crosslinked of PVA to the gelatin hydrogels impacted the rise in the
hydrogels compared to the non-crosslinked hydrogels, proportion of C components in the scaffolds. The crosslinked
indicating that the incorporation of GNP and PVA does hydrogels caused a minor decrease in carbon and a rise in
not alter the native amorphous property of the hydrogels. oxygen components, but no significant change was detected.
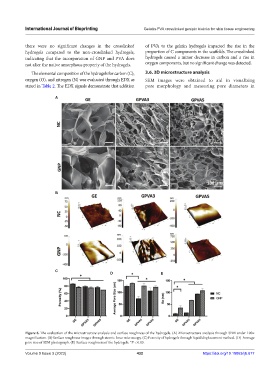
The elemental composition of the hydrogels for carbon (C), 3.6. 3D microstructure analysis
oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N) was evaluated through EDX as SEM images were obtained to aid in visualizing
stated in Table 2. The EDX signals demonstrate that addition pore morphology and measuring pore diameters in
A
B
C
D E
Figure 6. The evaluation of the microstructure analysis and surface roughness of the hydrogels. (A) Microstructure analysis through SEM under 100×
magnification. (B) Surface roughness images through atomic force microscopy. (C) Porosity of hydrogels through liquid displacement method. (D) Average
pore size of SEM photograph. (E) Surface roughness of the hydrogels. *P < 0.05.
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 432 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.677