Page 242 - IJB-9-4
P. 242
International Journal of Bioprinting Applications of 3D printing in aging
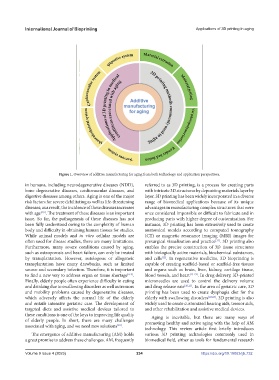
Figure 1. Overview of additive manufacturing for aging from both technology and application perspectives.
in humans, including neurodegenerative diseases (NDD), referred to as 3D printing, is a process for creating parts
bone degenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and with intricate 3D structures by depositing materials layer by
digestive diseases among others. Aging is one of the major layer. 3D printing has been widely incorporated in a diverse
risk factors for severe debilitating as well as life-threatening range of biomedical applications because of its unique
diseases; as a result, the incidence of these diseases increases advantages in manufacturing complex structures that were
with age [4,5] . The treatment of these diseases is an important once considered impossible or difficult to fabricate and in
issue. So far, the pathogenesis of these diseases has not producing parts with higher degree of customization. For
been fully understood owing to the complexity of human instance, 3D printing has been extensively used to create
body and difficulty in obtaining human tissues for studies. anatomical models according to computed tomography
While animal models and in vitro cellular models are (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images for
often used for disease studies, there are many limitations. presurgical visualization and practice . 3D printing also
[11]
Furthermore, many severe conditions caused by aging, enables the precise construction of 3D tissue structures
such as osteoporosis and heart failure, can only be treated with biologically active materials, biochemical substances,
by transplantation. However, autologous or allogeneic and cells . In regenerative medicine, 3D bioprinting is
[12]
transplantation have many drawbacks, such as limited capable of creating scaffold-based or scaffold-free tissues
source and secondary infection. Therefore, it is important and organs such as brain, liver, kidney, cartilage tissue,
to find a new way to address organ or tissue shortage [6-9] . blood vessels, and heart [13-19] . In drug delivery, 3D-printed
Finally, elderly people often experience difficulty in eating microneedles are used to control the delivery volume
and drinking due to swallowing disorders as well as tremors and drug release rate [20,21] . In the area of geriatric care, 3D
and mobility problems caused by degenerative diseases, printing has been used to create dysphagia diet for the
which adversely affects the normal life of the elderly elderly with swallowing disorders [22,23] . 3D printing is also
and entails intensive geriatric care. The development of widely used to create customized hearing aids, tremor aids,
targeted diets and assistive medical devices tailored to and other rehabilitation and assistive medical devices.
these conditions is one of the keys to improving life quality Aging is inevitable, but there are many ways of
of elderly people. In short, there are many challenges promoting healthy and active aging with the help of AM
associated with aging, and we need new solutions .
[10]
technology. This review article first briefly introduces
The emergence of additive manufacturing (AM) holds various 3D printing technologies commonly used in
a great promise to address these challenges. AM, frequently biomedical field, either as tools for fundamental research
Volume 9 Issue 4 (2023) 234 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.732