Page 244 - IJB-9-4
P. 244
International Journal of Bioprinting Applications of 3D printing in aging
Ref [25-28] [29,30] [31-34] [24,35,36] [37-41] [42,43] [44] [45-48] [49-52]
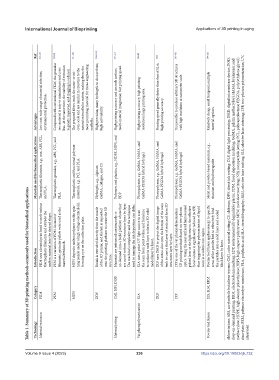
Low cost; wide range of material selection; Compared with conventional FDM, the granular raw material is easy to manufacture and costs less. At the same time, the stability of extrusion is greatly improved, and clogging is reduced. The prepared fibers reach the nano- or mi- cron-scale and are similar in structure to the natural extracellular matrix, making them the most promising material for tissue engineering High precision; many hydrogels to
Advantages environmental protection. scaffolds. high cell viability. high printing accuracy. material options.
Materials used for biomedical applications Thermoplastic filaments, e.g., wax, ABS, PCL, and PLA. Thermoplastic granules, e.g., ABS, PCL, and PLA. Thermoplastic and functional polymer materials, e.g., PCL and PLA. Hydrogels, e.g., alginate, GelMA, collagen, and CS. Polymers and plastics, e.g., HDPE, HIPS, and EDP. Photopolymer, e.g., GelMA, HAMA, and GelMA-PEGDA hybrid hydrogel. Photopolymer, e.g., GelMA, HAMA, and GelMA-PEGDA hybrid hydr
Table 1. Summary of 3D printing methods commonly used for biomedical applications
FDM uses a heated print head to melt various thermoplastic filaments and extrude the molten material into the desired shape. PEM is a variation of FDM. Instead of filaments, granular pellets were used as the MEW deposits molten polymer on the spin- ning nozzle under a high voltage electric field, forming a jet on the collection plate. Bioink is extruded directly from the nozzle of the 3D printer, and the ink is deposited onto the printing platf
Introduction material feedstock. structure. model layer by layer. structures layer by layer. resin in a submicron region. block layer by layer.
Category FDM PEM MEW DIW CMJ, NPJ, DOD SLA DLP 2PP SLS, SLM, EBM
Technology Material extrusion Material jetting Vat photopolymerization Powder bed fusion ultraviolet
Volume 9 Issue 4 (2023) 236 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.732