Page 332 - IJB-9-4
P. 332
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printing in bone regeneration and bone repair
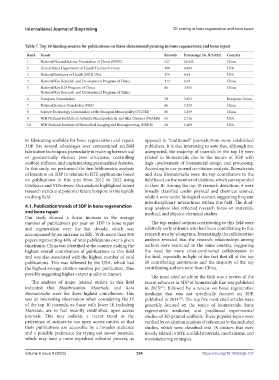
Table 7. Top 10 funding sources for publications on three-dimensional printing in bone regeneration and bone repair
Rank Funds Records Percentage (%, N/2,025) Country
1 National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) 527 26.025 China
2 United States Department of Health Human Services 180 8.889 USA
3 National Institutes of Health (NIH) USA 179 8.84 USA
4 National Key Research and Development Program of China 114 5.63 China
5 National Key R D Program of China 80 3.951 China
National Key Research and Development Program of China
6 European Commission 78 3.852 European Union
7 National Science Foundation (NSF) 66 3.259 China
8 Science Technology Commission of the Shanghai Municipality (STCSM) 66 3.259 China
9 NIH National Institute of Arthritis Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS) 55 2.716 USA
10 NIH National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) 50 2.469 USA
in fabricating scaffolds for bone regeneration and repair. opposed to “traditional” journals from more established
3DP has several advantages over conventional scaffold publishers. It is also interesting to note that, although not
fabrication techniques, particularly in realizing hierarchical unexpected, the majority of journals in the top 10 were
or geometrically distinct pore structures, controlling related to biomaterials due to the nature of 3DP with
scaffold stiffness, and implementing personalized features. high involvement of biomaterial design and processing.
In this study, we performed the first bibliometric analysis According to our journal co-citation analysis, Biomaterials
of literature on 3DP in relation to BTE applications based and Acta Biomaterialia were the top contributors to the
on publications in this area from 2012 to 2022 using field based on the number of citations, which corresponded
CiteSpace and VOSviewer. Our analysis highlighted recent to their IF. Among the top 10 research directions, 6 were
research trends and potential future hotspots in this rapidly broadly classified under physical and chemical science,
evolving field. while 4 were under biological science, suggesting frequent
interdisciplinary interactions within this field. The dual-
4.1. Publication trends of 3DP in bone regeneration map analysis also reflected research focus on materials,
and bone repair medical, and physico-chemical studies.
Our study showed a linear increase in the average
number of publications per year on 3DP in bone repair The top-ranked authors contributing to this field were
and regeneration over the last decade, which was relatively early entrants who had been contributing to this
accompanied by an increase in RRI. With more than 800 research area for a long time. Interestingly, the collaboration
papers representing 40% of total publications over a given analysis revealed that the research relationships among
timeframe, China was identified as the country making the authors were restricted to the same country, suggesting
highest overall contribution of publications to this field the need for more cross-continental collaboration in
and was also associated with the highest number of total the field, especially in light of the fact that all of the top
publications. This was followed by the USA, which had 10 contributing institutions and the majority of the top
the highest average citation number per publication, thus contributing authors were from China.
possibly suggesting higher output quality or impact.
The most cited article in the field was a review of the
The analysis of major journal outlets in this field recent advances in 3DP of biomaterials that was published
[35]
indicated that Biofabrication, Materials, and Acta in 2015 , followed by a review on bone regenerative
Biomaterialia were the three highest contributors. This medicine that was not specifically focused on 3DP,
was an interesting observation when considering the IF published in 2014 . The top five most cited articles were
[36]
of the top 10 journals, as those with lower IF, including generally focused on the topics of biomaterials, bone
Materials, are in fact recently established, open access regenerative medicine, and preclinical experimental
journals. This may indicate a recent trend in the studies of 3D-printed scaffolds. These popular topics were
preference of authors to use open access outlets so that verified by co-citation analysis of references to the included
their publications are accessible by a broader audience studies, which were classified into 18 clusters that were
and a possible preference for trying out newer journals, mostly related to BTE scaffold materials, mechanisms, and
which may have a more expedited editorial process, as manufacturing strategies.
Volume 9 Issue 4 (2023) 324 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.737