Page 342 - IJB-9-4
P. 342
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinting with machine learning
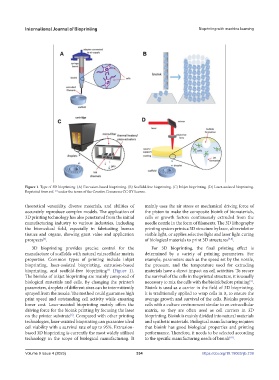
Figure 1. Type of 3D bioprinting. (A) Extrusion-based bioprinting. (B) Scaffold-free bioprinting. (C) Inkjet bioprinting. (D) Laser-assisted bioprinting.
[5]
Reprinted from ref. under the terms of the Creative Commons CC-BY license.
theoretical versatility, diverse materials, and abilities of mainly uses the air stress or mechanical driving force of
accurately reproduce complex models. The application of the piston to make the composite bioink of biomaterials,
3D printing technology has also penetrated from the initial cells or growth factors continuously extruded from the
manufacturing industry to various industries, including needle nozzle in the form of filaments. The 3D lithography
the biomedical field, especially in fabricating human printing system prints a 3D structure by laser, ultraviolet or
tissues and organs, showing great value and application visible light, or applies selective light and laser light curing
prospects . of biological materials to print 3D structures [7,8] .
[4]
3D bioprinting provides precise control for the For 3D bioprinting, the final printing effect is
manufacture of scaffolds with natural extracellular matrix determined by a variety of printing parameters. For
properties. Common types of printing include inkjet example, parameters such as the speed set by the nozzle,
bioprinting, laser-assisted bioprinting, extrusion-based the pressure, and the temperature used for extruding
[5]
bioprinting, and scaffold-free bioprinting (Figure 1). materials have a direct impact on cell activities. To secure
The bioinks of inkjet bioprinting are mainly composed of the survival of the cells in the printed structure, it is usually
biological materials and cells. By changing the printer’s necessary to mix the cells with the bioink before printing .
[9]
parameters, droplets of different sizes can be intermittently Bioink is used as a carrier in the field of 3D bioprinting.
sprayed from the nozzle. The method could guarantee high It is traditionally applied to wrap cells in it, to ensure the
print speed and outstanding cell activity while ensuring average growth and survival of the cells. Bioinks provide
lower cost. Laser-assisted bioprinting mainly offers the cells with a culture environment similar to an extracellular
driving force for the bioink printing by focusing the laser matrix, so they are often used as cell carriers in 3D
[6]
on the printer substrate . Compared with other printing bioprinting. Bioink is mainly divided into natural materials
technologies, laser-assisted bioprinting can guarantee ideal and synthetic materials. Biological manufacturing requires
cell viability with a survival rate of up to 95%. Extrusion- that bioink has good biological properties and printing
based 3D bioprinting is currently the most widely utilized performance. Therefore, it needs to be selected according
[10]
technology in the scope of biological manufacturing. It to the specific manufacturing needs of bioink .
Volume 9 Issue 4 (2023) 334 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.739