Page 157 - IJB-9-5
P. 157
International Journal of Bioprinting Guide about the effects of sterilization on 3D-printed materials for medicine
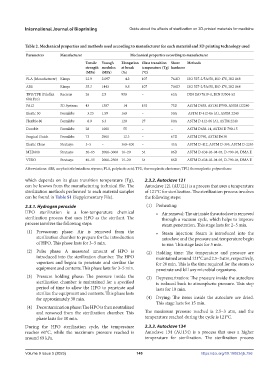
Table 2. Mechanical properties and methods used according to manufacturer for each material and 3D printing technology used
Parameters Manufacturer Mechanical properties according to manufacturer
Tensile Young’s Elongation Glass transition Shore Methods
strength modulus at break temperature (Tg) hardness
(MPa) (MPa) (%) (°C)
PLA (Manufacturer) Kimya 22.9 2.097 4.2 107 76.8D ISO 527-2/5A/50, ISO 178, ISO 868
ABS Kimya 35.3 1443 9.8 107 70.0D ISO 527-2/5A/50, ISO 178, ISO 868
TPU/TPE (Filaflex Recreus 26 2.5 950 – 63A DIN ISO 7619-1, DIN 53504-S2
60A Pro)
PA12 3D Systems 43 1387 14 192 73D ASTM D638, ASTM D790, ASTM D2240
Elastic 50 Formlabs 3.23 1.59 160 – 50A ASTM D 412-06 (A), ASTM 2240
Flexible 80 Formlabs 8.9 6.3 120 27 80A ASTM D 412-06 (A), ASTM 2240
Durable Formlabs 28 1000 55 – – ASTM D638-14, ASTM D 790-15
Surgical Guide Formlabs 73 2900 12.3 – 67D ASTM D790, ASTM D638
Elastic Clear Stratasys 3–5 – 360–400 – 45A ASTM D-412, ASTM D-395, ASTM D-2240
MED610 Stratasys 50–65 2000–3000 10–20 54 86D ASTM D-638-03-04-05, D-790-04, DMA E
VERO Stratasys 40–55 2000–2500 15–20 54 86D ASTM D-638-03-04-05, D-790-04, DMA E
Abbreviations: ABS, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene; PLA, polylactic acid; TPE, thermoplastic elastomer; TPU, thermoplastic polyurethane
which depends on its glass transition temperature (Tg), 2.3.2. Autoclave 121
can be known from the manufacturing technical file. The Autoclave 121 (AU121) is a process that uses a temperature
sterilization methods performed to each material samples of 121°C for sterilization. The sterilization process involves
can be found in Table S1 (Supplementary File). the following steps:
2.3.1. Hydrogen peroxide (1) Preheating:
HPO sterilization is a low-temperature chemical • Air removal: The air inside the autoclave is removed
sterilization process that uses HPO as the sterilant. The through a vacuum cycle, which helps to improve
process involves the following steps: steam penetration. This stage lasts for 2–5 min.
(1) Prevacuum phase: Air is removed from the • Steam injection: Steam is introduced into the
sterilization chamber to prepare for the introduction autoclave and the pressure and temperature begin
of HPO. This phase lasts for 3–5 min. to rise. This stage lasts for 5 min.
(2) Pulse phase: A measured amount of HPO is (2) Holding time: The temperature and pressure are
introduced into the sterilization chamber. The HPO maintained around 121°C and 2.5–3 atm, respectively,
vaporizes and begins to penetrate and sterilize the for 20 min. This is the time required for the steam to
equipment and contents. This phase lasts for 3–5 min. penetrate and kill any microbial organisms.
(3) Pressure holding phase: The pressure inside the (3) Depressurization: The pressure inside the autoclave
sterilization chamber is maintained for a specified is reduced back to atmospheric pressure. This step
period of time to allow the HPO to penetrate and lasts for 10 min.
sterilize the equipment and contents. This phase lasts
for approximately 30 min. (4) Drying: The items inside the autoclave are dried.
This stage lasts for 15 min.
(4) Decontamination phase: The HPO is then neutralized
and removed from the sterilization chamber. This The maximum pressure reached is 2.5–3 atm, and the
phase lasts for 10 min. temperature reached during the cycle is 121°C.
During the HPO sterilization cycle, the temperature 2.3.3. Autoclave 134
reaches 60°C, while the maximum pressure reached is Autoclave 134 (AU134) is a process that uses a higher
around 69 kPa. temperature for sterilization. The sterilization process
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 149 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.756