Page 164 - IJB-9-5
P. 164
International Journal of Bioprinting Guide about the effects of sterilization on 3D-printed materials for medicine
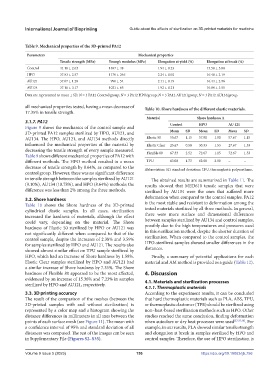
Table 9. Mechanical properties of the 3D-printed PA12
Parameters Mechanical properties
Tensile strength (MPa) Young’s modulus (MPa) Elongation at yield (%) Elongation at break (%)
Control 41.10 ± 2.63 1487 ± 48 1.94 ± 0.23 13.58 ± 5.80
HPO 37.83 ± 2.57 1170 ± 246 2.24 ± 0.02 16.48 ± 2.19
AU121 37.67 ± 1.28 990 ± 54 2.11 ± 0.19 16.44 ± 2.96
AU134 37.10 ± 3.17 1021 ± 65 1.92 ± 0.21 10.80 ± 3.51
Data are represented as mean ± SD. N = 3 PA12 Control/group; N = 3 PA12 HPO/group; N = 3 PA12 AU121/group; N = 3 PA12 AU134/group.
all mechanical properties tested, having a mean decrease of Table 10. Shore hardness of the different elastic materials.
17.35% in tensile strength.
Material Shore hardness A
3.1.7. PA12 Control HPO AU 121
Figure 9 shows the mechanics of the control sample and
3D-printed PA12 samples sterilized by HPO, AU121, and Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD
AU134. The HPO, AU121, and AU134 methods directly Elastic 50 55.67 1.15 57.00 1.00 57.67 1.15
influenced the mechanical properties of the material by Elastic Clear 25.67 0.58 30.33 1.53 27.67 1.53
decreasing the tensile strength of every sample measured.
Table 9 shows different mechanical properties of PA12 with Flexible 80 67.33 2.52 72.67 1.15 72.67 1.53
different methods. The HPO method resulted in a mean TPU 63.00 1.73 62.00 2.00 – –
decrease of tensile strength by 8.64%, as compared to the Abbreviation: SD, standard deviation; TPU, thermoplastic polyurethane.
control group. However, there was no significant difference
in tensile strength between the samples sterilized by AU121 The obtained results are summarized in Table 11. The
(9.10%), AU134 (10.78%), and HPO (8.64%) methods; the results showed that MED610 tensile samples that were
difference was less than 2% among the three methods. sterilized by AU134 were the ones that suffered more
3.2. Shore hardness deformation when compared to the control samples. PA12
Table 10 shows the Shore hardness of the 3D-printed is the most stable and resistant to deformation among the
cylindrical elastic samples. In all cases, sterilization tested materials sterilized by all three methods. In general,
increased the hardness of materials, although the effect there were more surface and dimensional differences
could vary, depending on the material. The Shore between samples sterilized by AU134 and control samples,
hardness of Elastic 50 sterilized by HPO or AU121 was possibly due to the high temperatures and pressures used
not significantly different when compared to that of the in this sterilization method, despite the shorter duration of
control sample, despite the increases of 2.38% and 3.59% sterilization. When compared to the control samples, the
for samples sterilized by HPO and AU121. The results also HPO-sterilized samples showed smaller differences in the
showed almost similar effect on TPU sample sterilized by distances.
HPO, which had an increase of Shore hardness by 1.58%. Finally, a summary of potential applications for each
Elastic Clear samples sterilized by HPO and AU121 had material and AM method is provided as a guide (Table 12).
a similar increase of Shore hardness by 7.35%. The Shore
hardness of Flexible 80 appeared to be the most affected, 4. Discussion
evidenced by an increase of 15.36% and 7.23% in samples 4.1. Materials and sterilization processes
sterilized by HPO and AU121, respectively.
4.1.1. Thermoplastic materials
3.3. 3D printing accuracy According to the experiment results, it can be concluded
The result of the comparison of the meshes (between the that hard thermoplastic materials such as PLA, ABS, TPU,
3D-printed samples with and without sterilization) is or thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) should be sterilized using
represented by a color map and a histogram showing the non–heat-based sterilization methods such as HPO. Other
distance differences in millimeters in all axes between the studies reached the same conclusion, finding deformation
points of each surface mesh (see Figure 11). The mean with when autoclave or dry heat processes were used [27,37,38] . For
a confidence interval of 95% and standard deviation of all example, in our results, PLA showed similar tensile strength
distances was computed. The rest of the images can be seen and elongation at break in samples sterilized by HPO and
in Supplementary File (Figures S2–S35). control samples. Therefore, the use of HPO sterilization is
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 156 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.756