Page 166 - IJB-9-5
P. 166
International Journal of Bioprinting Guide about the effects of sterilization on 3D-printed materials for medicine
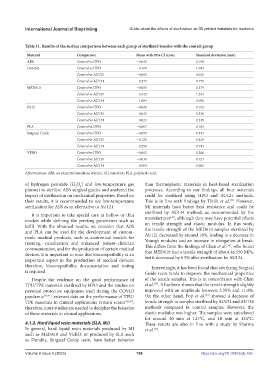
Table 11. Results of the surface comparison between each group of sterilized tensiles with the control group
Material Comparison Mean with 95% CI (mm) Standard deviation (mm)
ABS Control vs HPO −0.045 0.198
Durable Control vs HPO 0.160 1.044
Control vs AU121 −0.092 0.625
Control vs AU134 0.273 0.779
MED610 Control vs HPO −0.055 0.379
Control vs AU121 0.342 1.254
Control vs AU134 1.684 2.090
PA12 Control vs HPO −0.028 0.192
Control vs AU121 0.042 0.336
Control vs AU134 0.024 0.215
PLA Control vs HPO −0.007 0.165
Surgical Guide Control vs HPO −0.059 0.511
Control vs AU121 −0.126 0.529
Control vs AU134 0.258 0.741
VERO Control vs HPO −0.092 0.306
Control vs AU121 −0.036 0.721
Control vs AU134 0.509 0.905
Abbreviations: ABS, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene; AU, autoclave; PLA, polylactic acid.
of hydrogen peroxide [H O ] and low-temperature gas than thermoplastic materials in heat-based sterilization
2
2
plasma) to sterilize ABS surgical guides and analyzed the processes. According to our findings, all four materials
impact of sterilization on mechanical properties. Based on could be sterilized using HPO and AU121 methods.
their results, it is recommended to use low-temperature This is in line with findings by Török et al. However,
[44]
sterilization for ABS as an alternative to AU121. MJ materials have better heat resistance and could be
It is important to take special care in hollow or thin sterilized by AU134 method, as recommended by the
[45]
models while defining the printing parameters such as manufacturer , although they may have potential effects
infill. With the obtained results, we consider that ABS on tensile strength and elastic modulus. In this work,
and PLA can be used for the development of custom- the tensile strength of the MED610 samples sterilized by
made medical products, such as anatomical models for AU121 decreased by around 18%, leading to a decrease in
training, visualization and enhanced patient–clinician Young’s modulus and an increase in elongation at break.
[34]
communication, and for the production of certain medical This differs from the findings of Chan et al. , who found
devices. It is important to note that biocompatibility is an that MED610 had a tensile strength of about 46.550 MPa,
important aspect in the production of medical devices; but it decreased by 6.5% after sterilization by AU134.
therefore, biocompatibility documentation and testing Interestingly, it has been found that sterilizing Surgical
is required. Guide resin tends to improve the mechanical properties
Despite the evidence on the good performance of of the tensile samples. This is in concordance with Chan
[34]
TPU/TPE materials sterilized by HPO and the studies on et al. . It has been shown that the tensile strength slightly
personal protective equipment used during the COVID improved with an amplitude between 2.35% and 11.4%.
[32]
pandemic [40,41] , relevant data on the performance of TPU/ On the other hand, Pop et al. showed a decrease of
TPE materials in clinical applications remain scarce [42,43] ; tensile strength in samples sterilized by AU121 and AU134
therefore, more studies are needed to decipher the behavior methods compared to control samples. However, the
of these materials in clinical applications. elastic modulus was higher. The samples were autoclaved
for around 20 min at 121°C, and 10 min at 134°C.
4.1.2. Hard liquid resin materials (SLA, MJ) These results are also in line with a study by Sharma
In general, hard liquid resin materials produced by MJ et al. .
[33]
such as MED610 and VERO, or produced by SLA such
as Durable, Surgical Guide resin, have better behavior
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 158 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.756