Page 178 - IJB-9-5
P. 178
International Journal of Bioprinting Functional materials of 3D bioprinting for wound healing
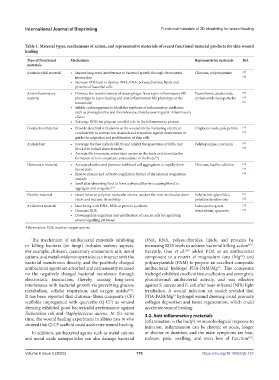
Table 1. Material types, mechanisms of action, and representative materials of recent functional material products for skin wound
healing
Type of functional Mechanism Representative materials Ref.
materials
Antimicrobial material • Impose long-term interference to bacterial growth through electrostatic Chitosan, polydopamine [47]
interaction [48]
• Increase ROS level to destroy DNA, RNA, polysaccharides, lipids and
proteins of bacterial cells
Anti-inflammatory • Promote the transformation of macrophages from a pro-inflammatory M1 Paeoniflorin, asiaticoside, [49]
material phenotype to a pro-healing and anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype at the cerium oxide nanoparticles [50]
wound site [51]
• Inhibit cyclooxygenase to block the synthesis of inflammatory mediators
such as prostaglandins and thromboxane, thereby exerting anti-inflammatory
effects
• Scavenge ROS that plays an eventful role in the inflammatory process
Conductive material • Provide electrical stimulation at the wound site by increasing electrical Graphene oxide, polypyrrole [52]
conductivity to activate ion channels and transduce signals downstream to [53]
guide the migration and proliferation of skin cells
Antioxidant • Scavenge the free radicals (ROS) and inhibit the generation of ROS, and Polydopamine, curcumin [55]
block free radical chain transfer [56]
• Activate the enzymatic antioxidant system in the body and stimulate the
[54
formation of non-enzymatic antioxidants in the body ]
Hemostatic material • Activate platelets and promote red blood cell aggregation to rapidly form Chitosan, kaolin, cellulose [58]
blood clots [59]
• Bind to plasma and activate coagulation factors of the internal coagulation [60]
cascade
• Swell after absorbing fluid to form a physical barrier, causing blood to
aggregate and coagulate [57]
Flexible material • Insert between polymer molecular chains, weaken the inter-molecular chain Poly(lactide-glycolide), [61]
stress and increase its mobility polydimethylsilox-ane [62]
Antitumor material • Interfering with DNA, RNA or protein synthesis Indocyanine green, [32]
• Generate ROS doxorubicin, quercetin [63]
• Downregulate migration and proliferation of cancer cells by regulating
several signaling pathways
Abbreviation: ROS, reactive oxygen species.
The mechanism of antibacterial materials inhibiting DNA, RNA, polysaccharides, lipids, and proteins by
or killing bacteria (or fungi) includes various aspects. increasing ROS levels to achieve bacterial killing action .
[48]
For example, chitosan, quaternary ammonium salt, metal Recently, Guo et al. added PDA as an antibacterial
[68]
cations, and metal oxide nanoparticles can interact with the component to a matrix of magnesium ions (Mg ) and
2+
bacterial membranes directly, and the positively charged polyacrylamide (PAM) to prepare an excellent composite
antibacterial agents are adsorbed and permanently retained antibacterial hydrogel PDA-PAM/Mg . This composite
2+
on the negatively charged bacterial membrane through hydrogel exhibited excellent tissue adhesion and synergistic
electrostatic interaction, thereby causing long-term photothermal antibacterial activity, and was effective
interference with bacterial growth via preventing glucose against S. aureus and E. coli after near-infrared (NIR) light
metabolism, cellular respiration, and oxygen uptake . irradiation. A wound infection rat model revealed that
[67]
It has been reported that chitosan–fibrin composite (CF) PDA-PAM/Mg hydrogel wound dressing could promote
2+
scaffolds impregnated with quercetin (Q-CF) as wound collagen deposition and tissue regeneration, which could
dressing exhibited good bactericidal performance against accelerate wound healing.
Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. At the same 3.2. Anti-inflammatory materials
time, the wound healing experiment in albino rats in vivo Inflammation is the body’s immunobiological response to
showed that Q-CF scaffold could accelerate wound healing. infection. Inflammation can be chronic or acute, longer
In addition, antibacterial agents such as metal cations or shorter in duration, and the main symptoms are heat,
[69]
and metal oxide nanoparticles can also damage bacterial redness, pain, swelling, and even loss of function .
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 170 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.757