Page 428 - IJB-9-5
P. 428
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printed topographically fabricated micron track peripheral nerve conduit
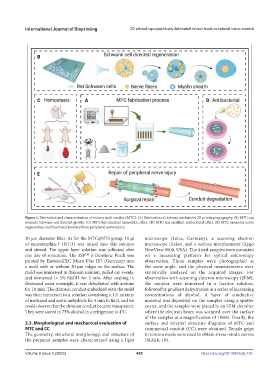
Figure 1. Fabrication and characterization of micron track conduit (MTC). (A) Fabrication of chitosan conduits by 3D printing topography. (B) MTC can
promote Schwann cell-directed growth. (C) MTC has excellent hemostatic effect. (D) MTC has excellent antibacterial effect. (E) MTC promotes nerve
regeneration and functional recovery from peripheral nerve injury.
20 μm diameter filter. As for the MTC@NT3 group, 10 µl microscope (Leica, Germany), a scanning electron
of neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) was mixed into this solution microscope (Zeiss), and a surface morphometer (Zygo
and stirred. The upper layer solution was collected after NewView 9000, USA). The dried samples were mounted
one day of sonication. The 3SP E-Denstone Peach was on a measuring platform for optical microscopy
TM
printed by EnvisionTEC Micro Plus HD (Germany) into observation. Three samples were photographed at
a mold with or without 30 μm ridges on the surface. The the same angle, and the physical measurements were
mold was immersed in chitosan solution, pulled out evenly, statistically analyzed on the acquired images. For
and immersed in 5% NaOH for 5 min. After soaking in observation with scanning electron microscopy (SEM),
deionized water overnight, it was dehydrated with acetone the samples were immersed in a fixative solution,
for 10 min. The chitosan conduit embedded with the mold followed by gradient dehydration in a series of increasing
was then immersed in a solution containing a 1:1 mixture concentrations of alcohol. A layer of conductive
of methanol and acetic anhydride for 5 min to fix it, and we material was deposited on the samples using a sputter
could observe that the chitosan conduit became transparent. coater, and the samples were placed in an SEM chamber
They were stored in 75% alcohol in a refrigerator at 4°C. where the electron beam was scanned over the surface
of the samples at a magnification of 1000x. Finally, the
2.3. Morphological and mechanical evaluation of surface and internal structure diagrams of MTC and
MTC and CC commercial conduit (CC) were obtained. Tensile grips
The geometry, structural morphology, and structure of in tension mode were used to obtain stress–strain curves
the prepared samples were characterized using a light (MALK-10).
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 420 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.770