Page 477 - IJB-9-5
P. 477
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printed hydrogel for infected wound healing via PDT
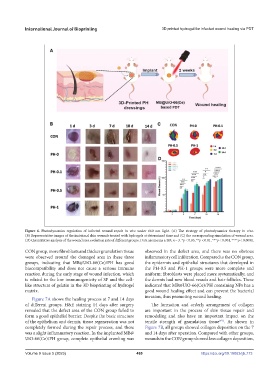
Figure 6. Photodynamics regulation of infected wound repair in vivo under 660 nm light. (A) The strategy of photodynamics therapy in vivo.
(B) Representative images of the incisional skin wounds treated with hydrogels at determined time and (C) the corresponding simulation of wound area.
(D) Quantitative analysis of the wound area evolution rate of different groups. Data are means ± SD; n = 3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
CON group, more fibroblasts and thicker granulation tissue observed in the defect area, and there was no obvious
were observed around the damaged area in these three inflammatory cell infiltration. Compared to the CON group,
groups, indicating that MB@UiO-66(Ce)/PH has good the epidermis and epithelial structures that developed in
biocompatibility and does not cause a serious immune the PH-0.5 and PH-1 groups were more complete and
reaction during the early stage of wound infection, which uniform; fibroblasts were placed more systematically; and
is related to the low immunogenicity of SF and the cell- the dermis had new blood vessels and hair follicles. These
like structure of gelatin in the 3D bioprinting of hydrogel indicated that MB@UiO-66(Ce)/PH containing NPs has a
matrix. good wound healing effect and can prevent the bacterial
invasion, thus promoting wound healing.
Figure 7A shows the healing process at 7 and 14 days
of different groups. H&E staining 14 days after surgery The formation and orderly arrangement of collagen
revealed that the defect area of the CON group failed to are important in the process of skin tissue repair and
form a good epithelial barrier. Despite the basic structure remodeling and also have an important impact on the
of the epithelium and dermis, tissue regeneration was not tensile strength of granulation tissue . As shown in
[49]
completely formed during the repair process, and there Figure 7B, all groups showed collagen deposition on the 7
was a slight inflammatory reaction. In the implanted MB@ and 14 days after operation. Compared with other groups,
UiO-66(Ce)/PH group, complete epithelial crawling was wounds in the CON group showed less collagen deposition,
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 469 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.773