Page 478 - IJB-9-5
P. 478
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printed hydrogel for infected wound healing via PDT
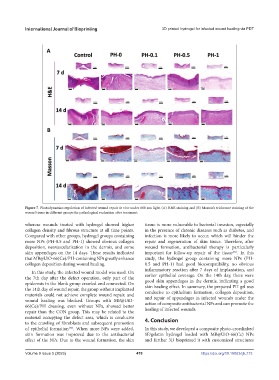
Figure 7. Photodynamics regulation of infected wound repair in vivo under 660 nm light. (A) H&E staining and (B) Masson’s trichrome staining of the
wound tissue in different groups for pathological evaluation after treatment.
whereas wounds treated with hydrogel showed higher tissue is more vulnerable to bacterial invasion, especially
collagen density and fibrous structure at all time points. in the presence of chronic diseases such as diabetes, and
Compared with other groups, hydrogel groups containing infection is more likely to occur, which will hinder the
more NPs (PH-0.5 and PH-1) showed obvious collagen repair and regeneration of skin tissue. Therefore, after
deposition, neovascularization in the dermis, and some wound formation, antibacterial therapy is particularly
[51]
skin appendages on the 14 days. These results indicated important for follow-up repair of the tissue . In this
that MB@UiO-66(Ce)/PH-containing NPs greatly enhance study, the hydrogel group containing more NPs (PH-
collagen deposition during wound healing. 0.5 and PH-1) had good biocompatibility, no obvious
inflammatory reaction after 7 days of implantation, and
In this study, the infected wound model was used. On
the 7th day after the defect operation, only part of the earlier epithelial coverage. On the 14th day, there were
good skin appendages in the dermis, indicating a good
epidermis in the blank group crawled and connected. On skin healing effect. In summary, the prepared PH gel was
the 14th day of wound repair, the group without implanted conducive to epithelium formation, collagen deposition,
materials could not achieve complete wound repair, and and repair of appendages in infected wounds under the
wound healing was blocked. Groups with MB@UiO- action of composite antibacterial NPs and can promote the
66(Ce)/PH dressing, even without NPs, showed better healing of infected wounds.
repair than the CON group. This may be related to the
material occupying the defect area, which is conducive 4. Conclusion
to the crawling of fibroblasts and subsequent promotion
of epithelial formation . When more NPs were added, In this study, we developed a composite photo-crosslinked
[50]
skin formation was improved due to the antibacterial SF/gelatin hydrogel loaded with MB@UiO-66(Ce) NPs
effect of the NPs. Due to the wound formation, the skin and further 3D bioprinted it with customized structures
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 470 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.773