Page 540 - IJB-9-5
P. 540
International Journal of Bioprinting GelMA/PEG-TA IPN networks for 3D bioprinting
3.8. Printability of GelMA and GelMA/PEGTA structure. The scaffold was post-UV crosslinked for 2 min.
5
solutions and bioinks Applying similar printing parameters with intermediate
The GelMA and GelMA/8PEGTA hydrogel precursor UV crosslinking and post-UV curing, stable structures
5
solutions, using PBS as a solvent, could be successfully printed could be prepared from GelMA/8PEGTA . The scaffold
5
with high shape fidelity (Figure S6, Supplementary File). was then submersed in a 0.03 wt% H O solution to create
2
2
On printing GelMA, the physically crosslinked network the IPN filaments.
formed at room temperature supported at least two layers, GelMA-UV and GelMA/8PEGTA -IPN scaffolds of
5
and intermediate 5 s UV crosslinking created a stable cubic shape are shown in Figure 6A. According to preset
A B
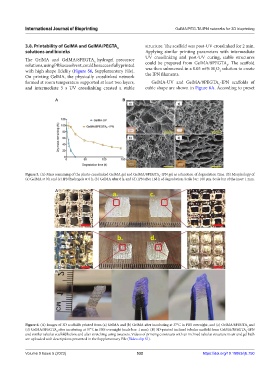
Figure 5. (A) Mass remaining of the photo-crosslinked GelMA gel and GelMA/8PEGTA -IPN gel as a function of degradation time. (B) Morphology of
5
(a) GelMA at 0 h and (c) IPN hydrogels at 0 h, (b) GelMA after 6 h, and (d) IPN after 168 h of degradation. Scale bar: 100 µm. Scale bar of the inset: 1 mm.
A
B
Figure 6. (A) Images of 3D scaffolds printed from (a) GelMA and (b) GelMA after incubating at 37°C in PBS overnight, and (c) GelMA/8PEGTA and
5
(d) GelMA/8PEGTA after incubating at 37°C in PBS overnight (scale bar: 1 mm). (B) 3D-printed inclined tubular scaffold from GelMA/8PEGTA -IPN
5
5
and similar tubular scaffold before and after stretching using tweezers. Videos of printing constructs with an inclined tubular structure in air and gel bath
are uploaded with descriptions presented in the Supplementary File (Video clip S1).
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 532 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.750