Page 133 - IJB-9-6
P. 133
International Journal of Bioprinting Exosome-based bioink for bioprinting
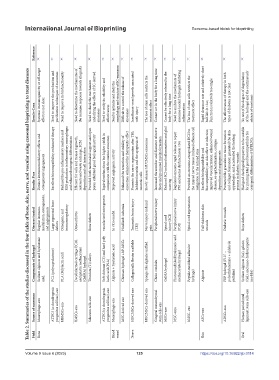
Reference [36] [67] [40] [68] [69] [70] [36] [72] [75] [78] [79] [76] [80] [77] [46] [90] [98]
[44] [115] [116] [117] [38] [118] [36]
Did not achieve the effective influence on the prognosis of traumatic brain injury (TBI). No statistical differences were displayed between hypo-Exo and Exo. Clinical trial data are lacking. The mechanical properties and stability need to be further improved. The purity and quality of exosomes need to be further studied and evaluated to ensure their safety and efficacy. Need to address the cost and safety of the method. Need to study the relationship be
Thermosensitive, injectable, self-healing, antioxidant, low cytotoxicity, and ultralong sustained release of SHED-Exo; enhanced the therapeutic potential of SHED-Exo. Improved angiogenesis, nerve regeneration, and functional motor restoration; Enhanced the therapeutic regenerative outcomes of MSC-derived exosomes, promoting the regeneration of the injured spinal cord. Promoted the healing of Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rat skin wounds, promoted th
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) Diabetes Myocardial infarction Thin endometrium Diabetic wound In vitro model Table 2. Summaries of the studies discussed in the four fields of bone, skin, nerve, and vascular using exosomal bioprinting to treat diseases Diseases treated Regular immuno- modulation, osteogenesis, and angiogenesis Large segmental bone defects Osteogenic and immunoregulatory Osteoarthritis Bone defect
Bioactive antioxidant poly(citric acid-gallic acid)- based hybrid hydrogel Binding peptide PPFLMLLKGSTR-modified hyaluronic acid hydrogel Chitosan/Silk Hydrogel Sponge PGN hydrogel (PA-GHRPS peptide+peptide NapFF) Four-arm SH-PEG cross-linked with Ag + hydrogel Anti-microbial peptide-based FHE hydrogel Alginate+hyaluronic acid Components of hydrogel Sodium alginate and hyaluronic acid. PCL (polycaprolactone) PLA (Polylactic acid) Decellularized c
SHED-Exo Hypoxia-stimulated MSCs-derived exosomes (sub-exo) Gingival mesenchymal stem cells(GMSCs)-Exos Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (UMSC- Exo) ADSC-exo AMSCs-exo Macrophage-exo Source of exosomes Macrophage-exo ATDC5 (a chondrogenic progenitor cell line)-exo HBMSCs-exo BMSCs-exo Schwann cells-exo ATDC5(a chondrogenic progenitor cell line)-exo Macrophage-exo MSC-derived exo HUCMSCs-derived exo HUCMSCs-derived
Field Bone Blood vessel Nerve Skin Oral
Blood vessel
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 125 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0114