Page 160 - IJB-9-6
P. 160
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printing in gastroenterology
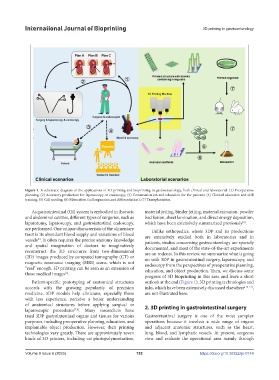
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of the applications of 3D printing and bioprinting in gastroenterology, both clinical and laboratorial. (1) Preoperative
planning; (2) Accessory production for laparoscopy or endoscopy; (3) Communication and education for the patients; (4) Clinical education and skill
training; (5) Cell seeding; (6) Maturation (cell expansion and differentiation); (7) Transplantation.
As gastrointestinal (GI) system is embodied in thoracic material jetting, binder jetting, material extrusion, powder
and abdominal cavities, different types of surgeries, such as bed fusion, sheet lamination, and direct energy deposition,
laparotomy, laparoscopy, and gastrointestinal endoscopy, which have been extensively summarized previously .
[9]
are performed. One unique characteristic of the alimentary Unlike orthopedics, where 3DP and its productions
tract is its abundant blood supply and variations of blood are extensively studied both in laboratories and in
vessels . It often requires the precise anatomy knowledge patients, studies concerning gastroenterology are sparsely
[5]
and spatial imagination of doctors to imaginatively documented, and most of the state-of-the-art experiments
reconstruct the 3D structures from two-dimensional are on rodents. In this review, we summarize what is going
(2D) images produced by computed tomography (CT) or on with 3DP in gastrointestinal surgery, laparoscopy, and
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, which is not endoscopy from the perspectives of preoperative planning,
“real” enough. 3D printing can be seen as an extension of education, and object production. Then, we discuss some
those medical images .
[6]
progress of 3D bioprinting in this area and leave a short
Patient-specific prototyping of anatomical structures outlook at the end (Figure 1). 3D printing technologies and
accords with the growing popularity of precision inks, which have been extensively discussed elsewhere [10-13] ,
medicine. 3DP models help clinicians, especially those are not illustrated here.
with less experience, perceive a better understanding
of anatomical structures before applying surgical or 2. 3D printing in gastrointestinal surgery
laparoscopic procedures [7,8] . Many researchers have
tried 3DP gastrointestinal organs and tissues for various Gastrointestinal surgery is one of the most complex
purposes, including preoperative planning, education, and operations because it involves a wide range of organs
implantable object production. However, their printing and adjacent anatomic structures, such as the heart,
technologies vary greatly. There are approximately seven lung, blood, and lymphatic vessels. At present, surgeons
kinds of 3D printers, including vat photopolymerization, view and evaluate the operational area mainly through
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 152 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0149