Page 216 - IJB-9-6
P. 216
International Journal of Bioprinting Multi-Cellular tissues/organoids manufacturing strategies
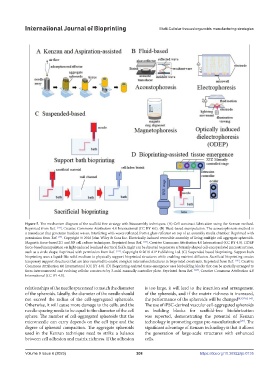
Figure 5. The mechanism diagram of the scaffold-free strategy with bioassembly techniques. (A) Cell construct fabrication using the Kenzan method.
Reprinted from Ref. [113] , Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0). (B) Fluid-based manipulation. The acoustophoresis method is
a transducer that generates incident waves, interfering with waves reflected from a glass reflector on top of an assembly media chamber. Reprinted with
permission from Ref. [77] . Copyright © 2016 John Wiley & Sons Inc. Electrically induced reversible assembly of living multiple cell aggregate spheroids.
Magnetic force-based 2D and 3D cell culture techniques. Reprinted from Ref. [114] . Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0). ODEP
force-based manipulation via light-induced localized electrical fields. Light can be directed to generate arbitrarily shaped cell-encapsulated microstructures,
such as a circle shape. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [115] . Copyright © 2018 AIP Publishing Ltd. (C) Suspended-based bioprinting. Support bath
bioprinting uses a liquid-like solid medium to physically support bioprinted structures while enabling nutrient diffusion. Sacrificial bioprinting creates
temporary support structures that are later removed to enable complex internal architectures in bioprinted constructs. Reprinted from Ref. [116] , Creative
Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0). (D) Bioprinting-assisted tissue emergence uses biobuilding blocks that can be spatially arranged to
form interconnected and evolving cellular constructs by 3-axial manually controller plate. Reprinted from Ref. [117] , Creative Commons Attribution 4.0
International (CC BY 4.0).
relationships of the needle space need to match the diameter is too large, it will lead to the insertion and arrangement
of the spheroids. Ideally, the diameter of the needle should of the spheroids, and if the matrix richness is increased,
not exceed the radius of the cell-aggregated spheroids. the performance of the spheroids will be changed [43,57,62-64] .
Otherwise, it will cause more damage to the cells, and the The use of iPSC-derived vascular cell-aggregated spheroids
needle spacing needs to be equal to the diameter of the cell as building blocks for scaffold-free biofabrication
sphere. The number of cell-aggregated spheroids that the was reported, demonstrating the potential of Kenzan
microneedle can carry depends on the cell type and the technology in promoting organ pre-vascularization . The
[29]
degree of spheroid compaction. The aggregate spheroids significant advantage of Kenzan technology is that it allows
used in the Kenzan technique need to strike a balance the generation of large-scale structures with enhanced
between cell adhesion and matrix richness. If the adhesion cells.
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 208 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0135