Page 353 - IJB-9-6
P. 353
International Journal of Bioprinting Surface modification of PCL scaffolds
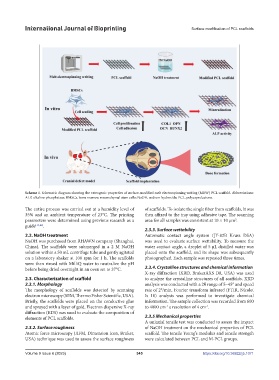
Scheme 1. Schematic diagram showing the osteogenic properties of surface-modified melt electrospinning writing (MEW) PCL scaffold. Abbreviations:
ALP, alkaline phosphatase; BMSCs, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; NaOH, sodium hydroxide; PCL, polycaprolactone.
The entire process was carried out at a humidity level of of scaffolds. To isolate the single fiber from scaffolds, it was
35% and an ambient temperature of 23°C. The printing then affixed to the tray using adhesive tape. The scanning
2
parameters were determined using previous research as a area for all samples was consistent at 10 × 10 µm .
guide [13,42] .
2.3.3. Surface wettability
2.2. NaOH treatment Automatic contact angle system (JY-82B Kruss DSA)
NaOH was purchased from RHAWN company (Shanghai, was used to evaluate surface wettability. To measure the
China). The scaffolds were submerged in a 2 M NaOH water contact angle, a droplet of 5 μL distilled water was
solution within a 50 mL centrifuge tube and gently agitated placed onto the scaffold, and its shape was subsequently
on a laboratory shaker at 100 rpm for 1 h. The scaffolds photographed. Each sample was repeated three times.
were then rinsed with MilliQ water to neutralize the pH
before being dried overnight in an oven set to 37°C. 2.3.4. Crystalline structures and chemical information
X-ray diffraction (XRD, BrukerAXS D8, USA) was used
2.3. Characterization of scaffold to analyze the crystalline structures of all scaffolds. XRD
2.3.1. Morphology analysis was conducted with a 2θ range of 5–45° and speed
The morphology of scaffolds was detected by scanning rate of 2°/min. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR, Nicolet
electron microscopy (SEM, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). Is 10) analysis was performed to investigate chemical
Briefly, the scaffolds were placed on the conductive glue information. The sample collection was recorded from 600
-1
-1
and sprayed with a layer of gold. Electron dispersive X-ray to 4000 cm a resolution of 4 cm .
diffraction (EDS) was used to evaluate the composition of
elements of PCL scaffolds. 2.3.5 Mechanical properties
A uniaxial tensile test was conducted to assess the impact
2.3.2. Surface roughness of NaOH treatment on the mechanical properties of PCL
Atomic force microscopy (AFM, Dimension Icon, Bruker, scaffold. The tensile Young’s modulus and tensile strength
USA) technique was used to assess the surface roughness were calculated between PCL and M-PCL groups.
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 345 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1071