Page 401 - IJB-9-6
P. 401
International Journal of Bioprinting Biofabrication for islet transplantation
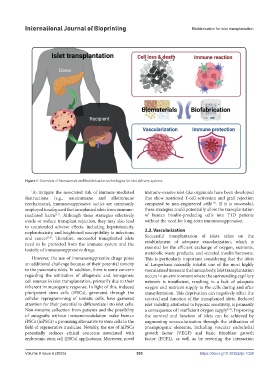
Figure 1. Overview of biomaterials and biofabrication technologies for islet delivery systems.
To mitigate the associated risk of immune-mediated immune-evasive islet-like organoids have been developed
destructions (e.g., autoimmune and alloimmune that show restricted T-cell activation and graft rejection
mechanisms), immunosuppressive tactics are commonly compared to non-engineered cells . If it is successful,
[14]
employed to safeguard the transplanted islets from immune- these strategies could potentially allow the transplantation
mediated harm . Although these strategies effectively of human insulin-producing cells into T1D patients
[13]
evade or reduce transplant rejection, they may also lead without the need for long-term immunosuppression.
to unintended adverse effects, including hepatotoxicity,
nephrotoxicity, and heightened susceptibility to infections 2.2. Vascularization
and cancer . Therefore, successful transplanted islets Successful transplantation of islets relies on the
[14]
need to be protected from the immune system and the establishment of adequate vascularization, which is
toxicity of immunosuppressive drugs. essential for the efficient exchange of oxygen, nutrients,
metabolic waste products, and secreted insulin hormone.
However, the use of immunosuppressive drugs poses This is particularly important considering that the islets
an additional challenge because of their potential toxicity of Langerhans naturally inhabit one of the most highly
to the pancreatic islets. In addition, there is some concern vascularized tissues in the human body. Islet transplantation
regarding the utilization of allogeneic and xenogeneic occurs in an environment where the surrounding capillary
cell sources in islet transplantation, primarily due to their network is insufficient, resulting in a lack of adequate
inherent immunogenic response. In light of this, induced oxygen and nutrient supply to the cells during and after
pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), generated through the transplantation. This deprivation can negatively affect the
cellular reprogramming of somatic cells, have garnered survival and function of the transplanted islets. Reduced
attention for their potential to differentiate into islet cells. islet viability, attributed to hypoxic sensitivity, is primarily
Non-invasive collection from patients and the possibility a consequence of insufficient oxygen supply . Improving
[15]
of autografts without immunomodulation make human the survival and function of islets can be achieved by
iPSCs (hiPSCs) a promising alternative to stem cells in the augmenting revascularization through the utilization of
field of regenerative medicine. Notably, the use of hiPSCs proangiogenic elements, including vascular endothelial
potentially reduces ethical concerns associated with growth factor (VEGF) and basic fibroblast growth
embryonic stem cell (ESCs) applications. Moreover, novel factor (FGF2), as well as by restoring the interaction
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 393 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1024