Page 93 - IJB-9-6
P. 93
International Journal of Bioprinting Review of 3D bioprinted organoids
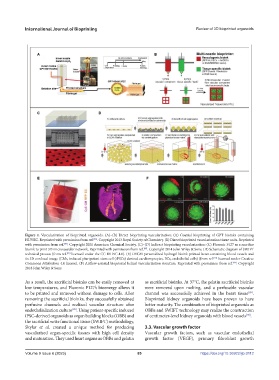
Figure 4. Vascularization of bioprinted organoids. (A)–(B) Direct bioprinting vascularization: (A) Coaxial bioprinting of GPT bioinks containing
HUVEC. Reprinted with permission from ref. . Copyright 2013 Royal Society of Chemistry. (B) Direct bioprinted vascularization tissue units. Reprinted
[86]
with permission from ref. . Copyright 2021 American Chemical Society. (C)–(D) Indirect bioprinting vascularization: (C) Pluronic F127 as a sacrifice
[87]
bioink to print 3D microvascular network. Reprinted with permission from ref. . Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons. (D) Schematic diagram of SWIFT
[88]
technical process (from ref. licensed under the CC BY-NC 4.0). (E) DECM personalized hydrogel bioink-printed heart containing blood vessels and
[89]
its 3D confocal image (CMs, induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSCs) derived cardiomyocytes, ECs, endothelial cells) (from ref. licensed under Creative
[93]
Commons Attribution 4.0 license). (F) Airflow-assisted bioprinted helical vascularization structure. Reprinted with permission from ref. . Copyright
[94]
2018 John Wiley & Sons.
As a result, the sacrificial bioinks can be easily removed at as sacrificial bioinks. At 37°C, the gelatin sacrificial bioinks
low temperatures, and Pluronic F127’s bioenergy allows it were removed upon melting, and a perfusable vascular
to be printed and removed without damage to cells. After channel was successfully achieved in the heart tissue .
[89]
removing the sacrificial bioinks, they successfully obtained Bioprinted kidney organoids have been proven to have
perfusive channels and realized vascular structure after better maturity. The combination of bioprinted organoids as
[88]
endothelialization culture . Using patient-specific induced OBBs and SWIFT technology may realize the construction
iPSC-derived organoids as organ building blocks (OBB) and of centimeter-level kidney organoids with blood vessels .
[90]
the sacrificial write functional tissue (SWIFT) methodology,
Skylar et al. created a unique method for producing 3.3. Vascular growth factor
vascularized organ-specific tissues with high cell density Vascular growth factors, such as vascular endothelial
and maturation. They used heart organs as OBBs and gelatin growth factor (VEGF), primary fibroblast growth
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 85 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0112