Page 95 - IJB-9-6
P. 95
International Journal of Bioprinting Review of 3D bioprinted organoids
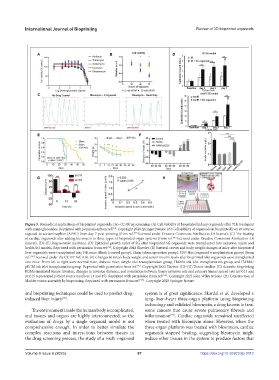
Figure 5. Biomedical applications of bioprinted organoids. (A)–(C) Drug screening: (A) Cell viability of bioprinted kidney organoids after 72 h treatment
with aminoglycosides. Reprinted with permission from ref. . Copyright 2020 Springer Nature. (B) Cell viability of organoids in bioprinted liver structures
[14]
exposed to acetaminophen (APAP) from day 7 post-printing (from ref. licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 license). (C) The beating
[98]
of cardiac organoids after adding bleomycin to three types of bioprinted organ systems (from ref. licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0
[99]
license). (D)–(F) Regenerative medicine: (D) Epithelial growth index of SG after bioprinted SG organoids were transplanted into radiation injury and
health SG models. Reprinted with permission from ref. . Copyright 2018 Elsevier. (E) Survival curves and body weight changes of mice after bioprinted
[52]
liver organoids were transplanted into F/R mice. Blank (control group), Sham (sham operation group), 3DP-Hos (organoid transplantation group) (from
ref. [101] licensed under the CC BY-NC 4.0). (F) Changes in mice’s body weight and serum insulin levels after bioprinted islet organoids were transplanted
into mice. From left to right were normal mice, diabetic mice, simple islet transplantation group, HAMA ink islet transplantation group, and HAMA/
pECM ink islet transplantation group. Reprinted with permission from ref. . Copyright 2022 Elsevier. (G)–(H) Tumor studies: (G) Acoustic bioprinting
[91]
PDMs simulated tumor invasion, changes in invasion distance, and correlation between tumor invasion rate and primary tumor spread rate (p(v)13 and
p(v)15 represented patient source numbers 13 and 15). Reprinted with permission from ref. [103] . Copyright 2022 John Wiley & Sons. (H) Construction of
bladder tumor assembly by bioprinting. Reprinted with permission from ref. [105] . Copyright 2020 Springer Nature.
and bioprinting techniques could be used to predict drug- system is of great significance. Skardal et al. developed a
[98]
induced liver injury . lung–liver–heart three-organ platform using bioprinting
technology and validated bleomycin, a drug known to treat
The environment inside the human body is complicated, some cancers that cause severe pulmonary fibrosis and
and tissues and organs are highly interconnected, so the inflammation . Cardiac organoids remained unaffected
[99]
evaluation of drugs by a single organoid model is not when treated with bleomycin alone. However, when the
comprehensive enough. In order to better simulate the three-organ platform was treated with bleomycin, cardiac
complex reactions and interactions between tissues in organoids stopped beating, suggesting bleomycin might
the drug screening process, the study of a multi-organoid induce other tissues in the system to produce factors that
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 87 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0112